 |
Plant Physiology (Biology 327) - Dr. Stephen G. Saupe; College of St. Benedict/ St. John's University; Biology Department; Collegeville, MN 56321; (320) 363 - 2782; (320) 363 - 3202, fax; ssaupe@csbsju.edu |
 |
Plant Physiology (Biology 327) - Dr. Stephen G. Saupe; College of St. Benedict/ St. John's University; Biology Department; Collegeville, MN 56321; (320) 363 - 2782; (320) 363 - 3202, fax; ssaupe@csbsju.edu |
Quiz: Soil & Plant Water Uptake
True/False Questions: Answer the following True (T) or False (F). Then, correct any false questions.
| 1. | water movement through a plant is driven by an active pumping system | |
| 2. | soil is a mixture of organic and inorganic molecules | |
| 3. | silt particles are larger than clay particles | |
| 4. | loam and humus are synonymous | |
| 5. | saturated soil has a very negative water potential | |
| 6. | at field capacity, the water potential is ca. -0.01 MPa | |
| 7. | the field capacity of sand, silt and clay is the same | |
| 8. | the amount of water held by sand, silt and clay at field capacity is the same | |
| 9. | the permanent wilting percentage (pwp) for most plants is -5 MPa | |
| 10. | all plants have the same PWP | |
| 11. | sand holds water more tightly than clay | |
| 12. | soil water potential is a function of osmotic potential and pressure (or matric potential which refers to the tension generated because of the adhesion of water to soil particles |
Diagram Question: The diagram below represents a cross section of a typical eudicot root.
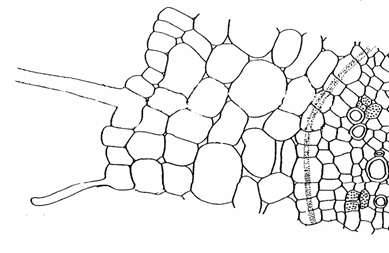
- Casparian strip
- cortex
- epidermis
- endodermis
- pericycle
- phloem
- stele
- xylem
- water moving from soil to xylem following an apoplastic route
- water moving from soil to xylem following a symplastic route
- water moving from soil to xylem following a transmembrane route
Short Answer Question: Using complete sentences,
answer the following questions.
Osmometer Question: The root is analogous to an osmometer (see diagram). For each of the following root structures, indicate the component of the osmometer to which it is analogous (glass tube, membrane, water in beaker).
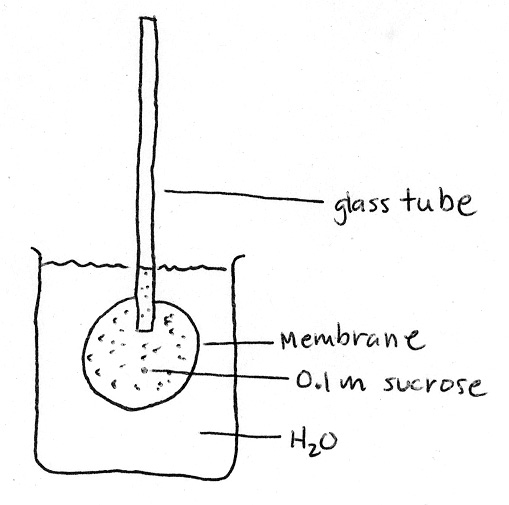
| Root Structure | Analogous Osmometer Structure |
| cortex | |
| endodermis | |
| xylem | |
| symplast | |
| apoplast |
Drawing Question: Draw a long section of a root tip. Include and label the following structures: root cap, root hairs, zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of differentiation, zone of maturation. Where does the greatest water uptake occur?
| | Top | SGS Home | CSB/SJU Home | Biology Dept | Biol 327 Home | Disclaimer | |
Last updated:
01/07/2009 � Copyright by SG
Saupe