Simple carbonyl groups contain a carbon double bonded to an oxygen. That C=O unit is commonly called a carbonyl. However, the carbonyl carbon is attached either to two carbons, in which case the compound is called a ketone, or to a carbon and a hydrogen, in whch case the compound is called an aldehyde. If the carbonyl carbon is attached to other heteroatoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen or a halogen, then it is called a carboxylic acid derivative or a carboxyloid.
It is useful to know the names of the normal (straight-chain) hydrocarbons, in which straight chains of hydrocarbons are connected by single bonds and the carbons' valences are saturated with hydrogens. The names of these compounds form the root names of other compounds having the same number of carbon atoms in a continuous chain.
| Number of carbons | Name |
| 1 | meth |
| 2 | eth |
| 3 | prop |
| 4 | but |
| 5 | pent |
| 6 | hex |
| 7 | hept |
| 8 | oct |
| 9 | non |
| 10 | dec |
The names of these compounds are based on the names of alkanes, but the suffix of the name varies to indicate the functional group present.
| Class | Icon | Description | Modified Prefix | Suffix |
| Carboxylic acid | RCO2H | contains C=O connected to one carbon and one OH group | - | oic acid |
| Amide | RCONR2 | contains C=O connected to one carbon and one nitrogen | N-alkyl | amide |
| Ester | RCO2R | contains C=O connected to one carbon and one OR group (R = hydrocarbon) | alkyl | oate |
Note that, in formal naming, amides and esters may contain modified prefixes. In amides, the prefix N-alkyl, such as N-methyl or N-propyl, denotes an additional carbon chain is attached to the nitrogen, as well as the chain that forms the root name of the compound. The main chain, forming the root of the name, is the part that contains the carbonyl.
In esters, the prefix alkyl, such as ethyl or butyl, denotes the chain that is attached to the ester group via an oxygen atom. The main chain, forming the root of the name, is the part that contains the carbonyl.
It is also important to realise that, despite the fact that a carboxylic acid contains an OH group, it is not considered to be an alcohol, because its behaviour is very different from that of an alcohol. It is not considered to be an aldehyde or ketone, either. In the same way, esters are not ethers and amides are not amines.
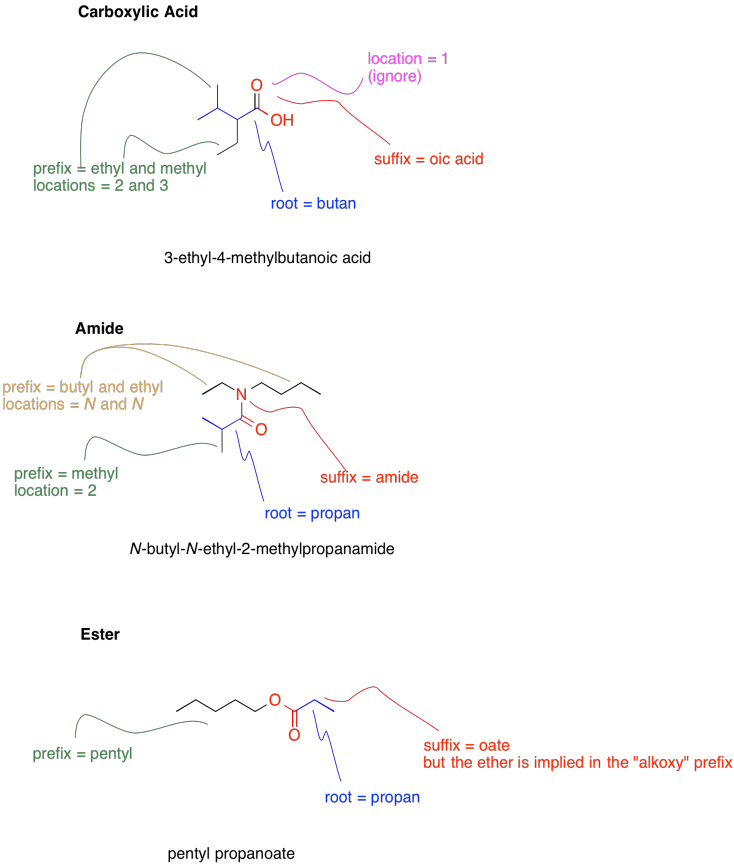
The following scheme provides representative examples of carboxylic acids, esters and amides as well as a brief guide to how the formal names of these compounds are put together based on their structures. Note that the root name is based on the longest continuous chain that contains the functional group. Substituents are named according to how many carbons they contain in a straight chain, and numbered based on where they are found along the main chain, in which each carbon can be numbered from one end to the other. The main functional group is present is always given the lowest possible number. If more than one functional group is present, the one that contains the most bonds to oxygen usually gets priority.

Note that, if more than one of the same type of substituent are present, a prefix is used to tell how many of them are present.
| Number | Prefix |
| 2 | di |
| 3 | tri |
| 4 | tetra |
| 5 | penta |
| 6 | hexa |
| 7 | hepta |
This site is written and maintained by Chris P. Schaller, Ph.D., College of Saint Benedict / Saint John's University (with contributions from other authors as noted). It is freely available for educational use.

Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry by
Chris Schaller is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported License.
Send corrections to cschaller@csbsju.edu
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1043566.
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.Navigation:
Back to Functional Group Appendix
Back to Web Materials on Structure & Reactivity in Chemistry