|
Click link above
for enlarged backbone sequence
Spacefill
Red=Oxygen, Blue=Nitrogen,
Orange=Phosphate, Gray=Carbon, Green=Mg 2+.
Wireframe
The wire frame model gives
the basic structure of L1 ligase ribozyme. The model clearly
shows the RNA structure with the nucleotide pairings including
phosphate backbone.
Backbone
The P unit is colored green while
the Q unit is colored red. This backbone image shows that the
ligase ribozyme has quaternary structure, forming a dimer of two
units with identical primary structure, consisting of the P and Q
subunits. (note the "c" sub-units of P and Q point in opposite
directions).
Wireframe
with stems A, B and C
This model shows
the three different stems of the ribozyme. Magenta=stem A,
Violet=stem B, White=stem C.
Cartoon
The cartoon model shows the secondary
structure of the ribozyme. This model shows the complimentary
folding of the RNA backbone forming a partially helical structure.
The P unit is colored green while the Q unit is colored red. Finally,
seven Mg 2+ ions can be seen as blue spheres.
Wireframe with Spacefill heteroatoms
Backbone with "hinge" nucleotides
(wireframe) with Mg 2+
This image shows the two
identical hinge sites on P and Q. These nucleotides are
preserved in both the docked and undocked conformers of the ribozyme.
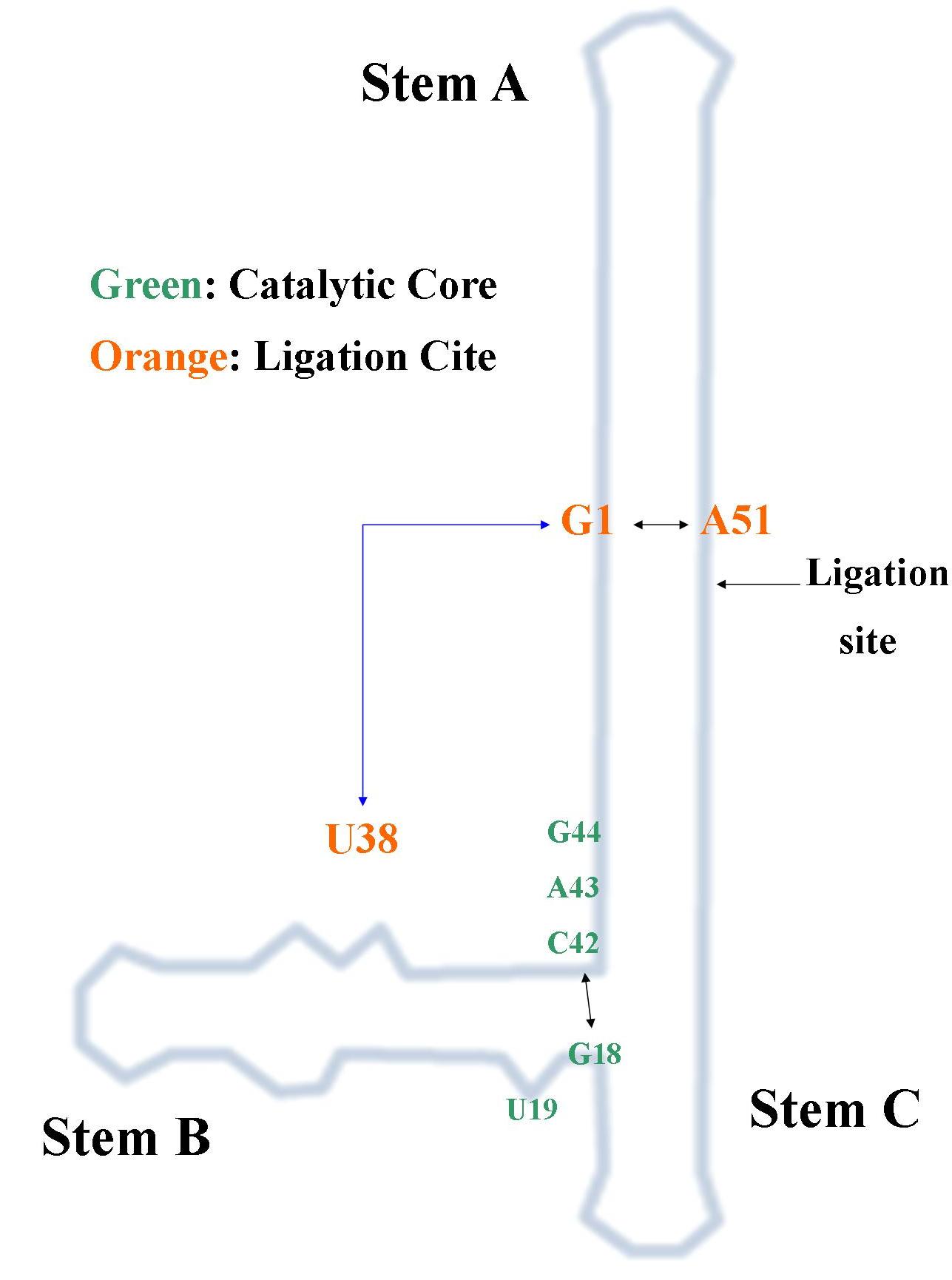
Backbone with base triple (U38:G1:A51)
This image shows
the tertiary contacts made by a base triple between nucleotides
U38:G1:A51. These contacts lock the ribozyme in its active
conformation (docked) for strand Q of the ribozyme. The Mg 2+
(blue) at the ligation site
along with water 13 (yellow) play a crucial role in stabalizing the active
site.
Authors:
Joseph M Brandt and Genevieve Saldanha
Works Cited
The Structural Basis of Ribozyme-Catalyzed RNA Assembly
Michael P. Robertson and William G. Scott (16 March 2007)
Science
315
(5818), 1549. [DOI: 10.1126/science.1136231]
A synthetic ribozyme catalyzes the bond
formation necessary for RNA synthesis by transition-state
stabilization and acid-base catalysis, perhaps as in an early RNA
world
|