
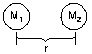
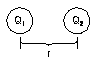
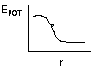
Force = -ΔE/ΔR
(or -ΔE/Δx) so
ΔE = -FΔx
or F = - slope (minus sign since F goes in opposite direction of
increasing potential.

Would you rather be hit by a mosquito or an elephant, each with a
velocity of 1 m/s?
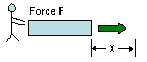
(Fext = friction), work done on rectangle



(picture of DeBroglie)
