This carboxylic acid derivative of glucose is fond in heparin and chondrotin sulfate.
These two different types of conformers of aldoses are clearly different from configuration isomers.
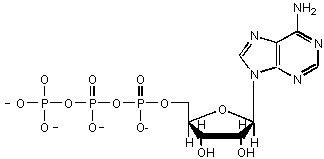
This sugar is in ATP

The name for this structures suggests
segregation
This polysaccharide is the major constituents of exoskeletons.
The name of the simplest ketose
This glycosidic link is found in cellulose.
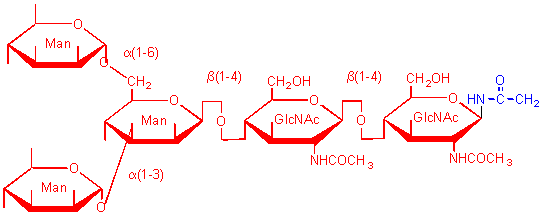
This structure is usually found in these
types of N-linked oligosaccharides
This reagent and catalyst can be used to cleave acetal links
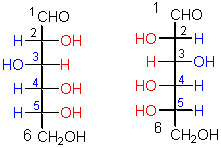
This pair represents a certain kind of
configurational isomers.
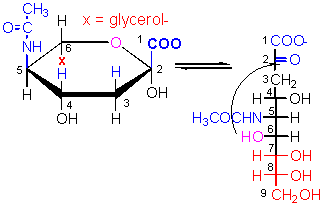
This is the net charge at physiological pH on the repeat dissacharide unit of heparin.
The penultimate C (and last chiral carbon) contains an OH that points to the right in this kind of sugar.
The name of this structure suggests
symmetry
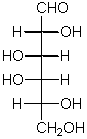
Bacteria cell walls contain a repeat of this dissacharide unit.
The dominant form of Glc in solution
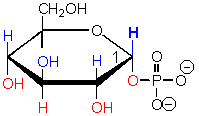
This sugar contains a phosphate group,
which are common in sugar derivatives as they undergo catabolic degradation in cells.
This polysaccharide is used for energy storage in plants
This link glycosidic link is found in glycogen and starch
This is the number of monosaccharides in the repeat unit of glycosoaminoglycans.
amide: peptide bond :: acetal: ______
This glycosoaminoglycan is found in synovial fluid
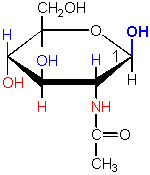
The name of this sugar implies that it is
a sugar-amine derivative
Found in bacteria, these structures contain both carbohydrate and amino acids.
The link between NAM on adjacent strands of a bacterial cell wall contains a pentapeptide of this amino acid.
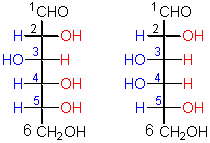
This pair represents a certain kind of
configurational isomers
Attached to NAN in Gram + bacterial cell walls, teichoic acid consists of a polymer of this molecule linked by phosphodiester bonds.
The dominate form of Glc in a polysaccharide
This reaction is typical of aldehydes and nucleophiles
This adds to a hemiacetal to form an acetal.
N-linked oligosaccharides ususally connect to a protein at this amino acid.
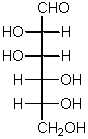
This is the simplest 3C aldose
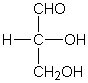
O-linked oligosaccharides usually connect to a protein at this amino acid.
The name of this sugar derivative implies
that it is an acid.
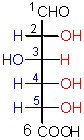
This sugar is found in all high mannose, N-linked oligosaccharides in glycoproteins.
This polysaccharide is used for energy storage in animals.
The name of this structure suggests
symmetry
The names of two unusual amino acids found in bacterial cell walls
Complex N-linked oligosaccharides in glycoproteins usually terminate in this sugar derivatives.
These two sites are where you would expect to find proteoglycans.
The only aldose with all bulky
substituents in the equatorial position
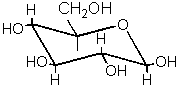
The dominant form of fructose in solution
The direction that an -OH group points in a Haworth projection if it points to the right in the aldose or ketose linear form
This glycosidic link connects monomers in the dissacharide repeat of heparin.
Water-soluble proteins can be attached to membranes by attaching a isoprenoid derivative to this amino acid.
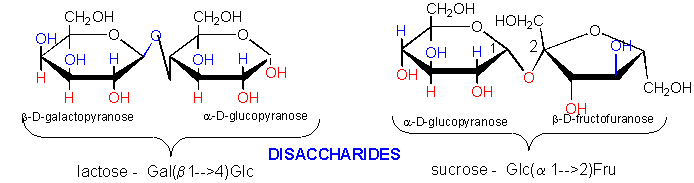
The disaccharide sucrose, Glc α(1--> 2) Frc can not do this, but the
disaccharide lactose, Gal β(1 -->
4) Glc can.
This kind of glycoprotein has an extensive amount of glycosoaminoglycan covalently attached to a protein core.
The dominant form of fructose in solution
The phospholipid is often attached to GlcNAc in soluble glycoproteins and anchors them to membranes.
This structure, derived from D-Man and
pyruvic acid, might prove to be the one which most separates human and chimps.
Of a eukaryotic, Gram (+) bacteria, or Gram (-) bacteria, the one with the most complicated membrane/cell wall structure.
The definition of a sugar
A 6-member heterocyclic ring containing oxygen and two double bonds within the ring.