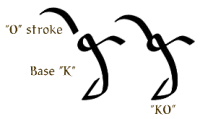

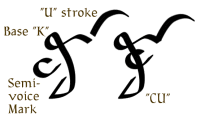
Right: The base T glides to voiced (D) form, as in "HOT DAY."

HAD -> HAND;
HAG -> HANG, etc.
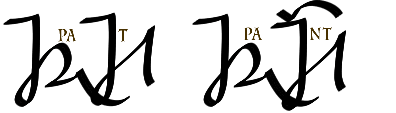

From L to R...


| The base consonant 'K' takes the positioned stroke for 'O' to form the sound 'KO.' | 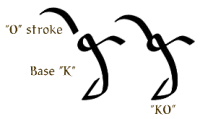 |
| The base consonant 'K' takes the voice mark to become 'G,' then the positioned stroke for 'A' to form the sound 'GA.' |  |
| The base consonant 'K' takes the semi-voice mark to become 'C,' then the positioned stroke for 'U' to form the sound 'CU.' | 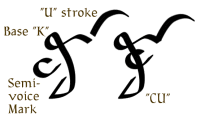 |
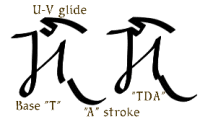
| Left: The base T glides from voiced
(D) to unvoiced (T) form, as in "RED TAG."
Right: The base T glides to voiced (D) form, as in "HOT DAY." |

 |
| The nasalizing mark adds an N sound
before some consonants - PAT becomes PANT, HAD -> HAND; HAG -> HANG, etc. |
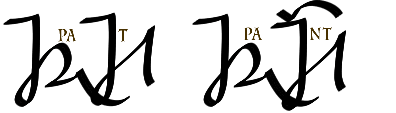 |
 From L to R... |
|
| 1. Use of terminal H mark to follow a vowel sound. GAH sounds like GA followed by a H sound. | |
| 2. Use of terminal H mark between a consonant and vowel sound. GHA has a softened, gargly G. | |
| 3. Use of H mark on initial vowel. HAG sounds like it looks: a green, scaly hag. | |
| 4. Use of leading H mark on consonant. Sounds like a sigh of relief ending in G. | |
| The consonant-repeater mark attaches to a vowel stroke. The consonant preceding the vowel is then repeated after the vowel. |  |
| If another vowel follows the repeated consonant, it's added to the consonant stroke... |  |
| ... unless the vowel is the same as the first vowel. In this case, the vowel stroke is added to the repeater mark. | 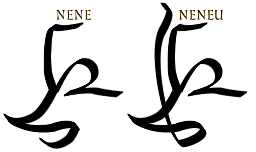 |