 |
Plant Physiology (Biology 327)
- Dr. Stephen G. Saupe; College of St. Benedict/ St.
John's
University; Biology Department; Collegeville, MN 56321; (320) 363 - 2782;
(320) 363 - 3202, fax;
ssaupe@csbsju.edu |
RCBr PRE LAB PREPARATION
I. READING: Read the
Lab Exercise and Directions for Growing Fast
Plants. For more information, check out the Wisconsin Fast Plant Manual
(available in the lab file) and visit the Wisconsin
Fast Plants� web site. This site provides a
wealth of information, including the on-line
version of the an article (Rapid-Cycling
Populations of Brassicas; Science, Vol. 232; 1986, pp.1385-89) by Dr. Paul Williams who
developed the plants, and slides/images
of the plants.
II. REVIEW: Review the structure of a flower and the flowering
plant life cycle (as necessary.)
III. QUESTIONS:
- Why do they call these plants "Fast plants"?
- To what family do these plants belong? (give the scientific and common name of this
family)
- List some characteristics of this family.
- Name two genera in this family.
- Give the common name of five common crops in the genus Brassica.
- Give the common name of two crops that are varieties of Brassica rapa.
- Give the scientific name of two other species of Brassica.
- Fast plants are self __________________ (compatible or incompatible).
- Name a plant that is self-compatible.
- Which diagram(s) best represents the breeding system of RCBr? Which would represent
maize? tomato?

- What is the function of the copper sulfate squares placed in the water reservoir?
- What is an achene?
- Draw the chemical structure of gibberellic acid (GA3).
- Draw the chemical structure of auxin (indole-3-acetic acid).
- Sketch in the predicted results in the following histogram. Two are done for you.
Explain the reason for your predictions.
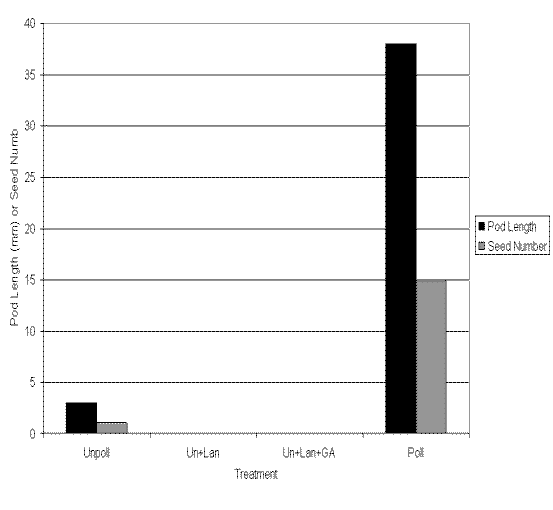
- Number the events listed below in sequence.
_____ fruit enlargement
_____
pollen tube growth
_____ fertilization
_____
pollination
_____ embryo development (embryogenesis)
- Answer the following questions True (T) or False (F)
_____ Parthenocarpic fruit have seeds.
_____ Parthenocarpic fruit are usually small and malformed.
_____ Parthenocarpic fruit require fertilization.
_____ Parthenocarpic fruit are typical in RCBr.
- Which pair can interbreed?
_____ turnip x broccoli _____ brussel sprouts
x black mustard
_____ kohlrabi x rutabaga _____ pak choi x collards
_____ cabbage x kale
- Why was the growth medium moistened before putting it into the pots/cells? What are
components of the growth medium?
- What does the symbol "+/+" refer to?
- What is Osmocote? Why is it labeled 14-14-14?
- Why did we wash the water mats with soap and water before using them?
- Describe the optimal light conditions for growing RCBr.
- Who developed RCBr? At what university? Why?
- What is parthenocarpy? Name the hormone(s) involved. Where are they produced? What is
their role? How do we know that they are involved?
- What do you predict will be the relationship between seed number and pod size?
- Will the pods be uniform in size? What might account for differences in sizes between
pods?
- We will plant several seeds in each cell even though we only want one plant. Why?
- When you thin the seedlings, how will you decide which seedling(s) to leave/remove?
- Why is it important to thin the seedlings to only one per cell?
- Sometimes, especially with root crops, it is necessary to add additional soil after
thinning. Why?
- What should we do with the seedlings after we remove them?
IV. SAFETY CONCERNS
Biological Materials: Fast plants are non-toxic. In fact, they are perfectly
edible (assuming the water and other materials to which they have been
exposed are not contaminated).
Chemicals:
- Lanolin - extracted from wool, harmless
- Gibberellic acid - avoid contact.
- Copper sulfate - used in reservoirs, is toxic. Avoid contact with mouth. Wash hands
after touching.
- White Glue - non-toxic
Safety Wear:
- Goggles or gloves not necessary in this experiment
Other:
- Although the flowers produce pollen, hay fever sufferers should not have any
problems.
Disposal:
- Water from reservoirs can be dumped down sink.
- Plants and soil can be thrown in trash, or better yet, put in our class composter
- Wash all materials with soap and water and allow to dry.
Last updated:
01/07/2009 � Copyright by SG
Saupe



