 Introduction
to Organismal Biology (BIOL221) -
Dr.
S.G. Saupe; Biology Department, College of St. Benedict/St. John's
University, Collegeville, MN 56321; ssaupe@csbsju.edu;
http://www.employees.csbsju.edu/ssaupe/ Introduction
to Organismal Biology (BIOL221) -
Dr.
S.G. Saupe; Biology Department, College of St. Benedict/St. John's
University, Collegeville, MN 56321; ssaupe@csbsju.edu;
http://www.employees.csbsju.edu/ssaupe/ |
 Introduction
to Organismal Biology (BIOL221) -
Dr.
S.G. Saupe; Biology Department, College of St. Benedict/St. John's
University, Collegeville, MN 56321; ssaupe@csbsju.edu;
http://www.employees.csbsju.edu/ssaupe/ Introduction
to Organismal Biology (BIOL221) -
Dr.
S.G. Saupe; Biology Department, College of St. Benedict/St. John's
University, Collegeville, MN 56321; ssaupe@csbsju.edu;
http://www.employees.csbsju.edu/ssaupe/ |
Grasshopper Dude
The following diagram is a "Saupian" model for the ear.
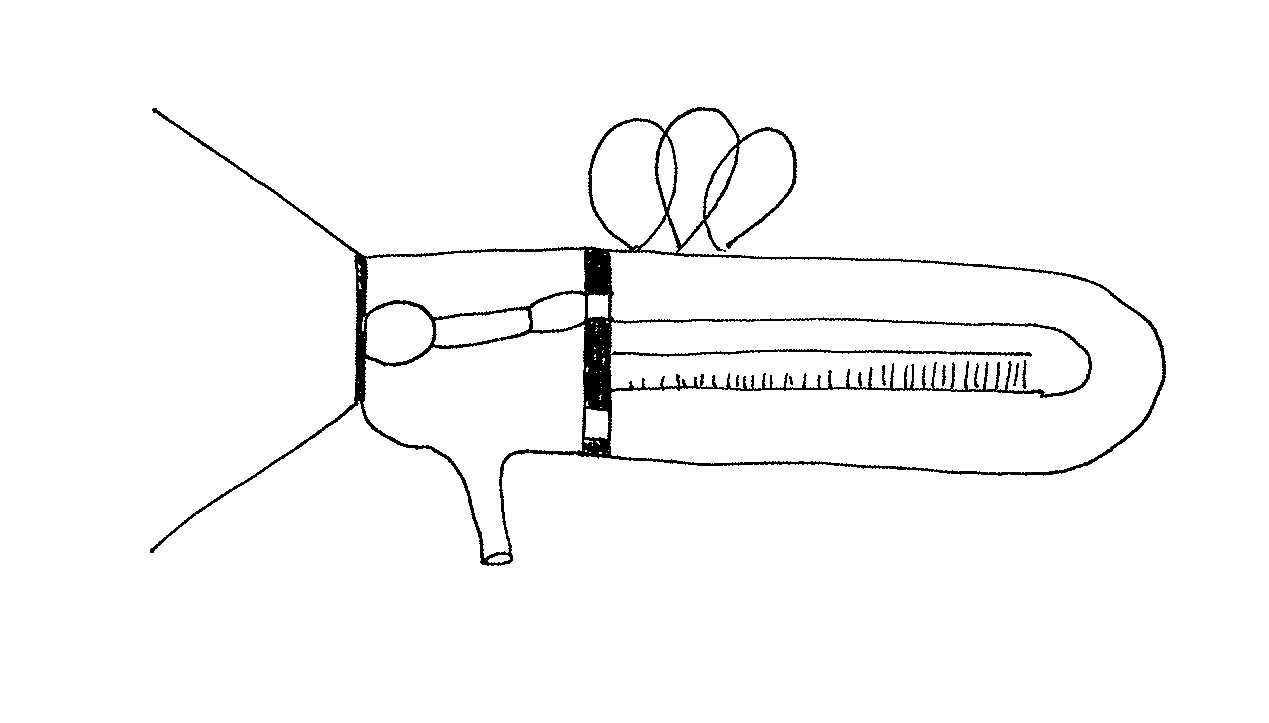
Diagram Labeling: Label the diagram with each of the following structures:
|
|
|
Questions:
Which structure (s) is involved in balance?
Which structure is coiled like a snail?
Which structure leads to the mouth? Why?
Which structure is especially prone to damage by loud sounds?
If you have tubes in your ears, in which structure would you find them? Why are they inserted?
Hearing "By-the-numbers": Number the following events in
sequence. The first one is done for you.
| _____ | Initiate action potential | _____ | Sound perception |
| _____ | Hair cells bend | _____ | Tympanic membrane vibrates |
| __1__ | Sound wave | _____ | Incus |
| _____ | Pressure waves in fluid of cochlea move from vestibular to tympanic canal | _____ | Oval window |
| _____ | Stapes | _____ | Depolarization |
| _____ | Hair cells from organ of Corti contact tectorial membrane | _____ | Brain |
| _____ | Basilar membrane vibrates | _____ | Malleus |
| | Top| SGS Home | CSB/SJU Home | Biology Dept | Biol221 Home | Disclaimer | |
Last updated: March 14, 2008 � Copyright by SG Saupe