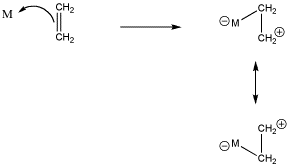CC5. Pi Coordination: Donation from Alkenes
Lone pairs are the most common electron donors in coordination complexes. Chloride ions, ammonia and phosphines all donate a lone pair to metals to form complexes. Lone pairs are not stabilized by bonding interactions already. Forming a bond lowers the energy of the lone pair electrons. On the other hand, bonding pairs are already lower in energy and so they are less likely to be donated.
However, pi bonds can also donate to Lewis acids. Donation from sigma bonds is still much less likely, though. Sigma bonds are buried between atoms and are hard to reach.
-
Pi bonds are often higher in energy than corresponding sigma bonds
-
Pi bonds are more accessible spatially than sigma bonds
A simple example of donation from a pi bond is the treatment of silver(I) salts with alkenes, shown in figure CC4.1.
Figure CC5.1. Formation of a silver alkene complex or "silver olefin" complex.
Strictly speaking, if an alkene donates its pi bonding electrons to a metal, we might draw it as shown in Figure CC4.2. The electrons are shared between two carbon atoms in the alkene. Since a bond is generally thought of as a pair of electrons shared between two atoms, then once the pi electrons are donated to the metal, they are shared between the metal and one of the carbons, but not both. If you are keeping track of electrons carefully, that leaves one of the carbons short on electrons. It must be a cation. Of course, either carbon could be the cationic one, so we can draw resonance structures showing both possible states.
-
donation of pi electrons to a metal can "activate" an alkene
-
the alkene can become positive and electrophilic
Figure CC5.2. Donation of a pair of pi-bonding electrons to a transition metal.
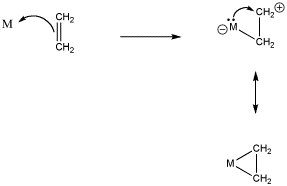
However, if a metal has valence electrons of its own, it could donate these electrons back to the "cation" that is forming on one of the alkene carbons. The alkene complex can be thought of as a "metallacycle" or a "metallacyclopropane", a three-membered ring containing two carbons and the transition metal atom.
-
alkene coordination also involves metal-to-alkene donation
Figure CC5.3. "Back-donation" of electrons from the metal to the alkene, in a Lewis sense.
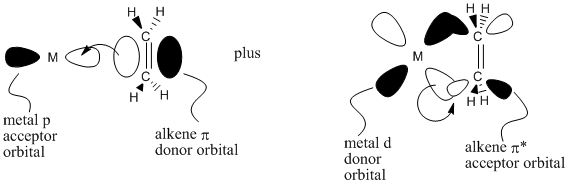
The idea of back-donation is also supported from a molecular orbital point of view. The alkene pi bond can donate electrons into an empty orbital on the metal, such as a p orbital. In turn, an occupied metal d orbital has the correct symmetry to overlap with a pi* orbital on the alkene. In doing so, we would think of the pi bond as breaking. We would also think of two pairs of bonding electrons between the metal and alkenes. This situation fits the picture of a metallacyle pretty well.
-
alkene-to-metal donation and metal-to-alkene donation are supported by molecular orbital calculations
-
without both components, alkenes do not bind very well to metals
-
nevertheless, the sigma bond formed by donation from the alkene is still the principle bond-forming event.
Figure CC5.4. "Back-donation" of electrons from the metal to the alkene, in an MO sense.
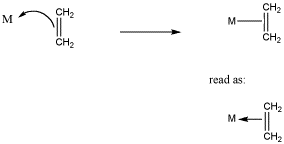
Remember that formalisms can be complicated in coordination complexes. For one thing, we do not usually draw positive formal charges on the donor atom or negative formal charges on the metal atom in the complex (unless specifically illustrating a point). In alkene complexes, bonding is usually illustrated with a line between the pi bond and the metal, as in Figure CC4.5. That line could be read as a pair of electrons, but it isn't, really. The pair of electrons is in the pi bond. They are being shared with the metal.
Figure CC5.5. Typical representation of alkene complexes.