Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
 Homework
Problems - Literature Learning Module: Transcription factor Ikaros
Represses Protein Phosphatase 2A
Homework
Problems - Literature Learning Module: Transcription factor Ikaros
Represses Protein Phosphatase 2A
Assessment of Biochemistry/Molecular Biology (BMB) Foundational Concepts
Henry Jakubowski, Ph.D., Professor, Chemistry Department, College of Saint Benedict/Saint John's University
This page contains assessment/exam questions using data, figures, and graphs from research journals such as the Journal of Biological Chemistry which allow their use, or from journals such as from PLOS that are completely open access The papers and topics chosen were selected to assess student understanding of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB) foundational concepts and learning objectives as well as MCAT2015 foundational concepts and objectives. These two sets of standards broadly overlap. Both ASBMB and the MCAT2015 strongly emphasis scientific inquiry and reasoning skills, which are perhaps best assessed by open-ended questions derived from the literature in which students must employ higher level Bloom skills of application and analysis.
These questions can also be used by students who seek more opportunities to practice interpreting research literature results. The ability to apply, analyze, and evaluate information and concepts are at the heart of scientific inquiry and reasoning skills which are central to the new ASBMB and MCAT2015 competency standards. The questions in this learning module are designed to assess these competencies using open-ended responses instead of multiple-choice questions. Answers can be found at the link at the bottom of this page.
Transcription factor Ikaros Represses Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Expression through an Intronic Binding Site
Transcription factor Ikaros Represses Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Expression through an Intronic Binding Site . Kamalpreet Nagpal, Katsue Sunahori Watanabe, Betty P. Tsao and George C. Tsokos. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289, 13751-13757 (2014).
Background and Review
Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease that primarily affects women in their reproductive years. Immune system irregularities, especially in T cells, are one of the contributing factors toward the pathology of this disease. In T cells isolated from SLE patients, aberrant signaling leads to atypical characteristics, such as enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation.
One of the key components contributing to the signaling defects in SLE pathogenesis is the serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). PP2A is a ubiquitously expressed, highly conserved serine/threonine phosphatase that plays a key role in a number of cellular processes like cell division, motility, cytoskeletal dynamics, etc. PP2A has a tripartite structure consisting of the scaffold subunit A and the catalytic subunit C forming the core enzyme and one of the many regulatory subunits binding to the core enzyme to form a functional holoenzyme. PP2A protein and mRNA levels as well as the enzymatic activity of the catalytic subunit are increased in T cells from SLE patients compared with healthy individuals.
A cyclic AMP (cAMP) response element (CRE) in the PP2A promoter is hypomethylated in SLE T cells. In addition binding of the transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein (CREBP) contributes to the expression levels of PP2A. cAMP increases in a cell in response to external signal which binds to a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) leading to activation of adenylate cyclase, forming cAMP. cAMP then binds to and activates Protein Kinase A which phosphorylates other proteins, including CREB protein which is mostly located in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylated CREB translocates to the nucleus leading to gene transciption.
a. Draw a cartoon showing how an increase in cAMP leads to transcription of CREB activated genes.
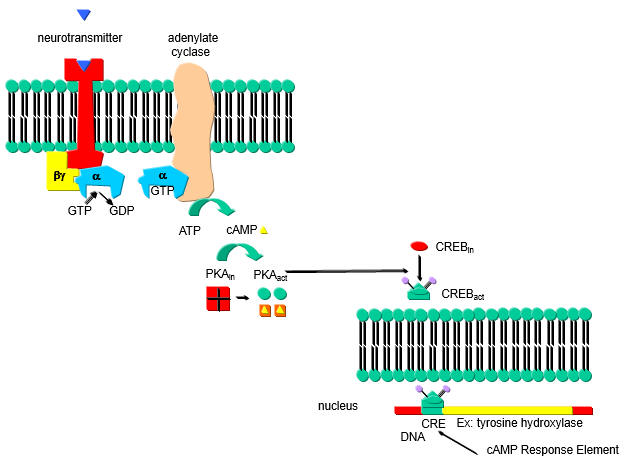
b. Hypomethylation of promoter enhances transcription. What would be the effect of hypermethylation of promoters of tumor suppressor genes on tumor cells? What effect might hypomethylation have on genes involved in immune cells in autoimmune diseases such as SLE?
Additional mechanisms affect the expression of PP2A. A genome wide association study (GWAS) study identified an single nucleotide polymorphorism (SNP) in the first intron of PPP2CA that was associated with SLE. The risk allele of this SNP was associated with renal disease, anti-double-stranded DNA, and anti-ribonucleoprotein antibodies, both markers of SLE. Moreover, PP2A expression was higher in patients carrying this allele, suggesting that this SNP may play a role in regulating PP2A expression. How could a mutation in an intron affect gene transcription?
Questions from article
1. Based on the SNP found in intron 1 of PP2A in SLE patients, the investigators hypothesized that binding of a transcription factor to the wild type intron 1 is involved in regulations of PP2A transcription.
a. State two different ways that a SNP in intron could affect PP2A transcription?
Figure 1A shows a schematic of the gene structure of PP2A (mislabeled in the original paper). The green boxes represent the introns.

The sequence containing the variant site is depicted in red and an arrow.
b. The investigators discovered a potential transcription factor, Ikaros, through in silico experiments that might bind to Intron 1. To study binding they used used a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. Briefly control and experimental cells were treated with formaldehyde to covalently attach DNA binding proteins to their target sites on DNA. Cells are first gently lysed to remove cytoplasmic proteins. 1% SDS is added to fully lyse the cells. This is followed by sonication to shear DNA into small fragments. An antibody to a target protein is added to the sheared chromatin and immunoprecipitated through a bead covalently attached to a protein (Protein A or G) that binds to the Fc domain which is not involved in recognition of the antibody for the target protein. The cross link can be reversed and the DNA binding site and/or target protein identified. Draw a cartoon showing the relevant interactions.
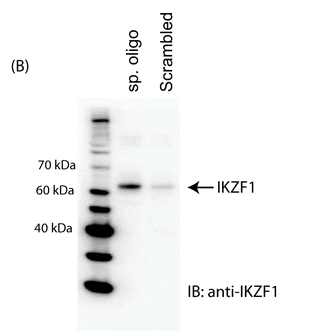
The investigators made a biotin-labeled oligo representing the relevant region of the normal intron 1 and a random control oligo. They added Jurkat cell nuclear extracts. The complex was pulled down (immunoprecipitated) with beads containing covalently attach avidin which binds biotin tightly. The eluates were run on a SDS PAGE gel followed by Western blot in which the separated proteins where transfered to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were probed membrane with an anti-Ikaros antibody. The immunoblot (IB) results are shown in Figure 1B. Interpret the results? If the authors' hypothesis was correct, what would the blot look like if they had used an oligo containing the SNP found in SLE?
2. The investigators constructed luciferase reporter constructors in which they linked the promoter for PP2A followed by Intron 1 as cloned just upstream of the gene for the protein luciferase, a bioluminescent protein that can be used to detect protein expression. Draw a cartoon of this construct.
In Figure 2B, 2 million 293T cells were transfected with either the reporter plasmid above by itself (250 ng) or in combination with different amounts of the Ikaros expression vector (containing 50, 100, or 200 ng of vector with the gene for Ikaros, IKZF1) using Lipofectamine 2000. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were collected and lysed, and luciferase activity was quantified by using the Dual-Luciferase assay system.
In Figure 2C, similar experiments were conducted in a transient expression assay with the mutant (mut) reporter construct in which the Ikaros binding site was deleted. The results represent mean � S.D. of three observations. The wedges indicate increasing concentrations. A control vector was also used that did not contain the PP2A promoter- Intron 1 insert.
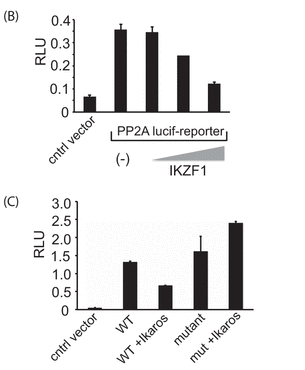
b. Explain the results shown in 2B.
c. Explain the results shown in 2C.
3. Investigators asked whether Ikaros can regulate the expression of PP2A. To this end, we overexpressed Ikaros in CD3+ T cells (immune cells) isolated from healthy individuals, not in reporter assays. After 36 h in culture, cells were collected and processed for immunoblotting. For Figure 3A (below), T cells isolated from healthy individuals were transfected with the empty vector or 0.5, 1, or 2 μg of the Ikaros expression plasmid/1 million cells. Five million cells were used per condition. 36 h post-transfection, cells were harvested to proceed with either real-time PCR (which monitors mRNA in real time, left panel) or protein analysis using Western blotting (center panel). For real-time PCR, the housekeeping gene β-actin was used for normalization. In the case of Western blot analyses, the membrane was probed with anti-Ikaros, stripped off the proteins, and re-probed with anti-PP2A. β-actin was used as a loading control. Band densities of IKZF1 and PP2A were quantified using Quantity One software and normalized to β-actin. Open bars, IKZF1; black bars, PP2A. IB, immunoblot.
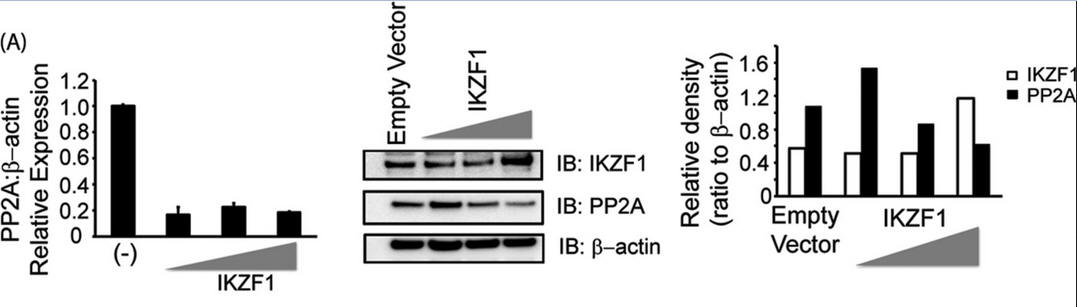
Explain the results. Why did the authors do an immunoblot for actin?
In Figure 3B, T cells were transfected with either scrambled siRNA or IKZF specific siRNA (5 or 10 nm final concentration) using AMAXA. 72 h after transfection, cells were harvested and subjected to either real-time PCR analysis or protein analysis using Western blotting. For real-time PCR, the housekeeping gene β-actin was used for normalization. In the case of Western blot analyses, the membrane was probed with anti-Ikaros, stripped off the proteins, and reprobed with anti-PP2A. β-actin was used as a loading control. Explain the results.
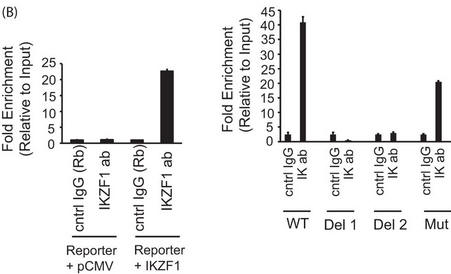
4. The authors employed a ChIP assays to confirm the recruitment of Ikaros to this particular site in a cellular setting. They used 293T cells transfected with the PP2A promoter-intron reporter construct (described above) in combination with either the empty vector (pCMV) or an Ikaros expression vector. Immunoprecipitates were made using an Ikaros antibody or a control IgG. Immunoprecipitated DNA was purified, and the presence of the specific intronic DNA was quantified using real-time PCR analysis.
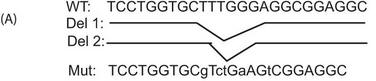
a. A schematic of the mutant (Mut) reporters used in these experiments is shown below.
b. In Figure 4B below, reporter ChIP in 293T cells. 293T cells were transfected with either only the wild type (left panel) or the mutant reporter (right panel) or the reporter in combination with the Ikaros expression plasmid using Lipofectamine 2000. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were collected, and a ChIP assay was performed. The region spanning the specific intron site was amplified by quantitative PCR and normalized to the values obtained from the input DNA. The graph shows mean � S.D. of three observations. cntrl, control; ab, antibody; Rb, rabbit. .
Interpret and explain the result.
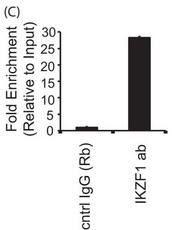
4C. For a more more physiologically relevant test, the authors studied the endogenous PPP2CA gene in T cells by ChIP assays in primary T cells and conducted immunoprecipitation of endogenous Ikaros protein using an Ikaros-specific antibody. 5 million freshly isolated primary T cells were used for each antibody/sample. There was no transfection, and endogenous proteins were used for immunoprecipitation of the chromatin. The region spanning the specific intron site was amplified by quantitative PCR and normalized to the values obtained from the input DNA. The graph shows mean + S.D. of three observations. Interpret and explain the result.
5. Ikaros is a zinc finger transcription factor that also harbors a dimerization domain at its carboxyl terminal through which it can recruit many different proteins and transcriptional regulators, including chromatin-modifying complexes like Sin3A, Sin3B, and histone deacetylase 1 or HDAC1.
- if HDAC binds to Ikaros as surmised above, what would be the likely effect of deacetylation of histones on the transcription of PP2A?
a. Transient transfections in HEK 293T cells, followed by immunoprecipitation assays were carried out. . Using biotinylated oligos, we also show that HDAC1 binds to the particular site in the first intron of PP2A (Fig. 5B). In both reporter ChIP as well as endogenous ChIP in primary T cells, we could see increased recruitment of HDAC1 to the intronic site compared with control IgG (Fig. 5C, left and right panels, respectively), thus confirming that HDAC1 does bind to this site in PP2A intron 1.
Figure 5A shows the results of a coimmunoprecipitation (IP) assay showing the binding of Ikaros with HDAC1. 293T cells were transfected with the various combinations of plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were lysed, and the supernatants were incubated with Ikaros antibody for 2 h at 4 �C. After the preincubation with the antibody, agarose A/G beads were added to each sample and incubated overnight at 4 �C. The immunoprecipitates were subsequently run on a gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and blotted for the indicated proteins. The saved inputs were also run on the gel to confirm equal expression of proteins in all samples. IB, immunoblot.
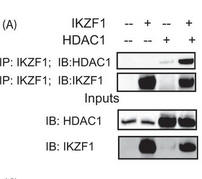
Interpret the results:
b. Figure 5B shows the results of a biotin-conjugated, intron-specific oligo (sp. oligo) or a random control oligo pulldown assays with Jurkat cell nuclear extracts. The eluates were run on a gel and probed with anti-HDAC1 antibody.
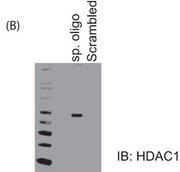
Explain the results.
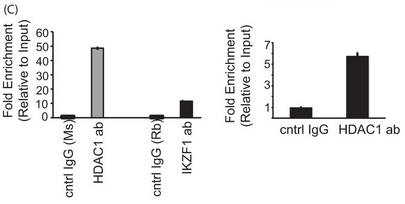
c. In Figure 5C results from a reporter ChIP (left panel) and ChIP (right panel) in 293T and primary T cells, respectively, are shown. 293T cells (left panel) were transfected with the reporter in combination with the Ikaros and HDAC1 expression plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were collected, and a ChIP assay was performed using the MAGnify ChIP kit. For ChIP with endogenous protein in primary T cells (right panel), 5 million freshly isolated primary T cells were used for each antibody (ab)/sample. The region spanning the specific intron site was amplified by quantitative PCR and normalized to the values obtained from the input DNA. The graph shows mean � S.D. of three observations. cntrl, control; Rb, rabbit; Ms, mouse. Explain the result.
d. In Figure 5D, T cells were transfected with control siRNA or 10 nm HDAC1-specific siRNA with or without cotransfection of the Ikaros plasmid. 72 h after transfection, cells were harvested and subjected to real-time PCR analysis. The housekeeping gene β-actin was used for normalization. Explain the results.
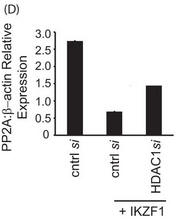
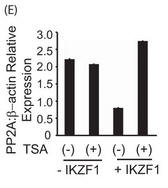
Figure 5E. E, primary T cells were transfected with the Ikaros plasmid using AMAXA. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were treated with 100 ng/ml trichostatin A (TSA) for 12 h. The same volume of dimethyl sulfoxide was used as in the vehicular control. The cells were harvested, and real-time PCR was carried out. The housekeeping gene β-actin was used for normalization. Explain the result.
6. Write a paragraph summarizing the main conclusions of this paper:
Navigation
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.