Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 2 - PROTEIN STRUCTURE
G: PREDICTING PROTEIN PROPERTIES FROM SEQUENCES
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
Last Update: 3/9/16
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 2G: After class and this reading, students will be able to:
|
G5. Prediction of Protein Tertiary Structure
We are getting closer to predicting the tertiary structure of a protein, but as we have seen from molecular mechanics and dynamics calculations, it is a huge computational task. There are two basic approaches which are often combined.
- calculations using energy minimization and statistical mechanics: These "semi-empirical" techniques don't assume any given secondary structure propensities or hydrophobicities. Such methods have produced limited success with small proteins whose actual structure is known.
- homology modeling based on proteins of known structure: The structures of about 117,00 (3/16) different biological macromolecules are known. This can serve as an empirical data base of possible conformations. Instead of an infinite number of prototypical structures, it is becoming clear that there may be a reasonably low number (in the hundreds) of basic structural motifs that are used over and over in nature. By aligning the amino acid sequences of different proteins, and comparing their properties (such as secondary structure propensities, hydrophobicities, etc.), probable low energy structures of the new protein can be determined. This initial structure can be run through multiple minimization and dynamic simulations to produce a tentative "lowest" energy structure. The structure should be compact (checked through calculation of packing density) and experimental techniques (such as spectroscopic methods) should be employed to validate the structure.
Many mechanisms of the actual folding process have been postulated, most of which have some experimental support. In one, a hydrophobic collapse of the protein produces a seed structure upon which secondary structure and final tertiary collapse results. Alternatively, initial formation of an alpha helix might serve as the seed structure. A combination of the two is likely. In one scenario, two small amphiphilic helices might form which interact through their nonpolar faces to produce the initial seed structure.
Many studies have been done on a domain of the protein villin. A company at Stanford University (Folding at Home) actually allows you to process protein folding data on your own computer when you're not using it (an example of distributed computing). The example below shows one simulation of length greater than 1 ms. In the simulation, it collapses to a near native-like state then unfolds again as it iteratively probes conformational space as it "seeks" the global energy minimum.
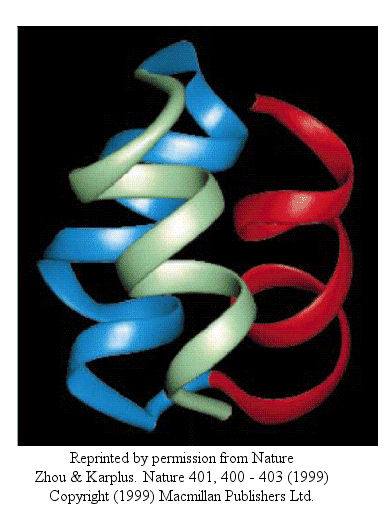
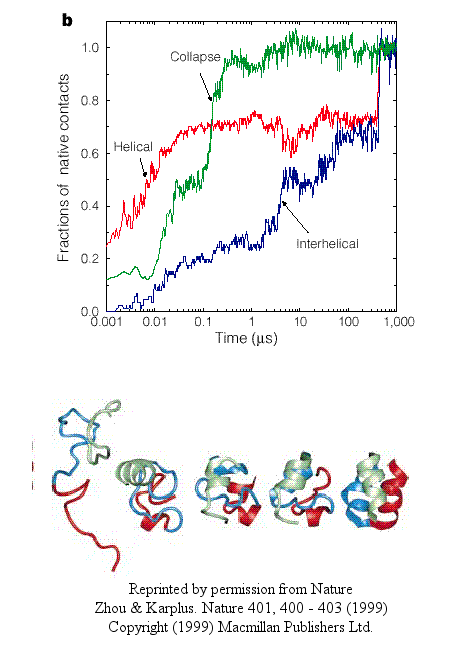
Zhou and Karplus simulated the folding of residues 10-55 of Staphylococcus aureus protein A which form a 3-helix bundle structure.
Figure: 3-helix bundle
Using molecular dynamics, they carried out 100 folding simulations. Two types of folding trajectories were noted.
- In the first type, helices form early (70% within 10 ns), but the fraction of native interhelical contacts (indicating proper packing of the helices together) and the overall packing density are not similar to the native state. Then the helices diffuse and collide with each (in the rate-limiting step) until the native state is reached at about 19 ms. In this model, non-obligatory intermediates can occur (due to collapse to non-native interhelical packing in the rate-limiting step) which could slow down folding.
Figure: helices form early
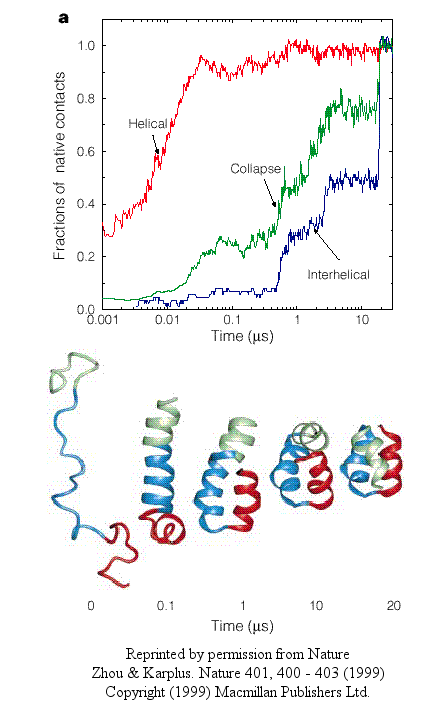
- In another type, there is a simultaneous and quick partial helix formation and collapse (90% at 200 ns), to a state which is similar to the molten globule. At this point, only about 20% of the native contacts are present. The final tertiary structure is achieved after a slow process of forming native contacts within the compact state, which takes about 500 ms.
Figure: simultaneous and quick partial helix formation and collapse
The Fersht lab has been combining experimental and theoretical approaches to the folding/unfolding of another three helix bundle protein, Engrailed homeodomain.
Figure: Engrailed homeodomain

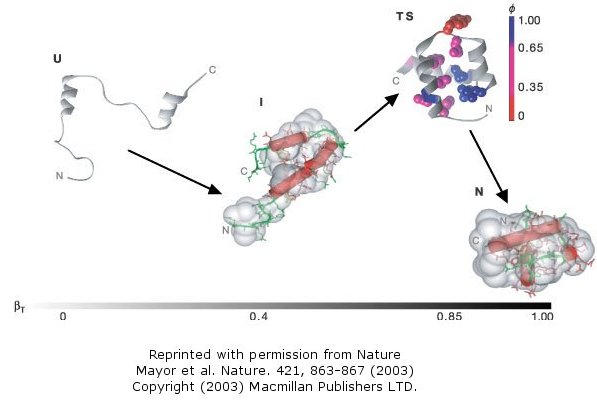
This protein is among the fastest folding and unfolding proteins known (ms time scale). This time frame is now also amenable to study through molecular dynamics simulations. Both sets of data support a folding pathway in which the unfolded state (U) collapses in a microsecond to an intermediate state (I) characterized by significant native secondary structure and mobile side chains that is less compact than the native state (N). The I state hence resembles the molten globule state. To more clearly understand the unfolded state, they generated a mutant (Leu16Ala) which was only marginally stable at room temperature (2.5 kcal/mol). Spectroscopic measurements (CD, NMR) showed this state to resemble the intermediate (I) state, with much native secondary structure and a 33% greater radius of gyration than the N state. In effect they could study the transient intermediate of the wild type protein more easily by making that state more stable through mutagenesis. These studies showed that the intermediate is on the folding pathway and not inhibitory to the process. Using molecular dynamic simulations, the intermediate to native state transition was shown to proceed via a transition state (TS) in which the native secondary structure is almost all present and the helices are engaged in the final packing process.
Figure: Complete Folding Pathway of Engrailed Homeodomain by Experiment and Simulation
Bradley et al (2005) have taken another step forward in prediction of
tertiary structure for small proteins
(< 85 amino acids). They
describe the two biggest stumbling blocks to such predictions as the huge
number of conformations which must be explored (i.e. all of conformational
space) and accurate determination of the energy of the solvated structures.
Searching conformational space is difficult since the energy landscape
around the global energy minimum can be very steep and sharp, since
modest side chain displacements arising from subtle main chain movements
cause significant side chain packing and energy changes. The
narrowness of the energy well makes it difficult to find the global minimum
in stochastic conformational search processes. Energy calculations
also require better (more realistic) energy functions (force fields) which
show the native state to be clearly differentiated as the global minimum
from the denatured (non-native) states. They conducted energy
calculations on many different small proteins and produced for each protein
a low resolution model. To reach this low resolution model for a given
protein, they found many sequence homologs of the given target protein.
These homologs were naturally occurring sequence variants found by a
relatively conservative BLAST sequence search, with sequence identities of
30-60 percent. They also contained insertions and deletions compared
to the target sequence, which probably are involved in surface loop
structures. The target and homolog sequences were folded,
generating a more diverse population of low-resolution models as starting
points for all-atom refinement of the structure. Then, using a
new force field that stressed short range interactions (van der Waals,
H-bonding), which would expected to be more important for final folding of
the low resolution models than long range electrostatic forces), they were
able to refine the models and condense to a final low energy that was very
close in main and side chain packing to the experimental crystal structure
(resolution < 1. angstroms).
The holy grail in protein folding research has always been to predict the tertiary structure of a protein given its primary sequence. A similar but conceptually easier problem is to design a protein which will fold to a given structure with predicted secondary structure. Many possible sequences could be designed to fold to the desired structure, which makes this problem easier compared to the folding of a given sequence to just one native state. Kuhlman et al. have recently accomplished such a feat for a synthetic protein of 93 amino acids which they designed to fold to a unique topology not yet observed in nature. This represents a significant advance over earlier attempts in which mimics of known proteins were made. Such structures would be expected to fold in analogous fashions to the parent protein because of the necessary constraints placed by the need to fold to a compact state.
![]() Jmol:
Updated Top7 - A designed 93 amino acid protein with a novel
fold
Jmol14 (Java) |
JSMol (HTML5)
Jmol:
Updated Top7 - A designed 93 amino acid protein with a novel
fold
Jmol14 (Java) |
JSMol (HTML5)
Several web sites exist that allow users to download protein folding software onto their own PC. By distributing folding calculations to many home PC, their untapped computational power can be linked to provide the vast computational time needed to perform these calculations.
Additional links:
- folding of nicotine acetylcholine receptor subdomain (new 2014)
- Rosetta@home with folding Ubiquitin
- K.A. Dill, S. Banu Ozkan, T.R.Weikl, J.D. Chodera and V.A. Voelz. The protein folding problem: when will it be solved?. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 17 : 342--346 (2007). (PDF)
Navigation
Return to Chapter 2G: Predicting Protein Properties from Sequences
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 2G: Predicting Protein Property from Sequences

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.