Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 9 - METABOLIC AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
A. ACTIVE TRANSPORT
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
04/16/16
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 9A:
|
A3. Transport of Sugars
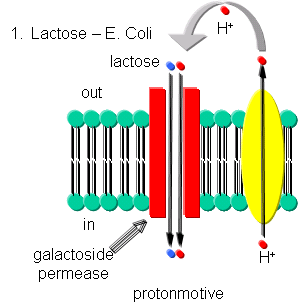
Lactose - Lactose can be transported into E. Coli against a concentration gradient using galactoside permease, one of the proteins encoded by the lac operon. This protein uses a proton-motive force to pump lactose into the cell. The proton gradient is created by an electron transport complex in the membrane which is inhibited by cyanide, reminiscent of the cytochrome C oxidase complex in oxphos.
Figure: Lactose Transport
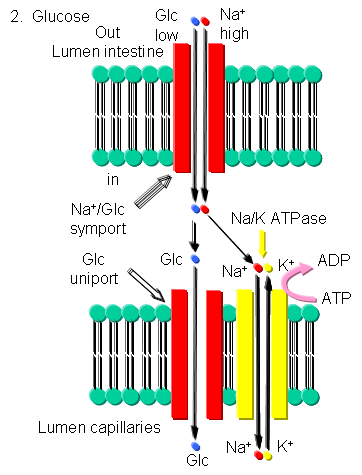
Glucose - Glucose can be transported into brush border cells lining the small intestine powered by a sodium-motive symport transporter.
Figure: Glucose Transport
Navigation
Return to Chapter 9A: Active Transport Sections
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 9A: Active Transport

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.