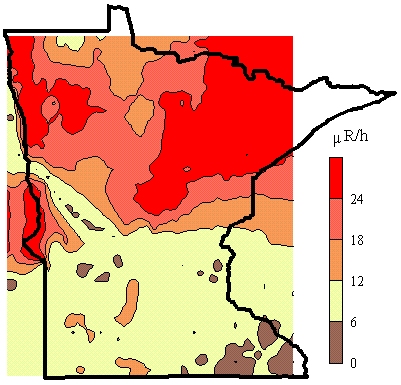

The gamma ray flux above 40 keV is used to determine the surface gamma ray exposure at 1m. We developed a carborne system for mapping gamma radiation from soil located next to streets and highways (Steck, 1993). The radionuclide concentrations were extracted from gamma ray spectra taken by a 7.6 x 7.6 cm NaI detector shielded to view the about 0.3 hectares of surface approximately 10 m beyond the right hand side of the automobile. Spectra were automatically acquired and analyzed by a onboard multichannel analyzer that was driven by batching software. Locations were determined every 40s by a global position receiver coupled to the portable computer. The flux is integrated during for 120 s. We sampled the flux along highways and town streets in the populated areas of Minnesota. This map reflects approximately 3000 data intervals of 1 to 2 km long. The total flux was converted to exposure by comparison with a calibrated survey meter (Ludlum model 12 S microR meter) at several locations. By restricting data acquisition to times of stable weather, the total exposures are reproducible to within 20%.

Questions/Comments, e-mail: Dr. Steck
Last revised : 30 June, 2004
Visitor
since
06/30/04
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed on the web sites hosted on this server are strictly those
of the author.
The contents of the web sites on this server have not been reviewed or
approved by the College of St. Benedict|St. John's University.