Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 8: OXIDATIVE-PHOSPHORYLATION
A: THE CHEMISTRY OF DIOXYGEN
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
04/14/16
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 8A: After class and this reading, students will be able to
|
A1. The History of Oxygen
Oxygen may be considered one of the most important element in chemistry. Not counting hydrocarbons, there is a greater diversity of molecules with oxygen than with carbon. Given its role in the molecular world, very little time is spend on the chemistry of oxygen in undergraduate chemistry classes. Why is oxygen so special?
Oxygen reacts with atoms of all elements except the Noble gases to form molecules. One of the most important molecules of course, from a biological sense is water. It :
- provides a perfect solvent for biomolecules
- moderates the earths climate
- is the source of almost all the dioxygen in the air
From a chemical point of view, water is a(n):
- nucleophile and electrophile
- acid and base
- oxidizing agent and reducing agent
- a protic solvent that can form H-bonds
The formation of earth and the development of life:
The gaseous and dusty environment from which earth formed contained metals and water, which as you remember from introductory chemistry, can react to form hydrogen gas. H2 reacts with nonmetals (under various conditions of temperature and pressure) to form H2S, HCl, CH4, and NH3 which contributed to the reducing nature of the early atmosphere. This kept the transition metals in their lowest oxidation states. Many metals, including the coinage metals (Cu, Ag, and Au) and the platinum group (Ru, Rh, Pd, Pt) were stable in elemental form.
Then, around 2.7-2.8 billion years ago, photosynthetic organisms (blue/green algae- also called cyanobacteria) developed which could oxidize water to form dioxygen. Oxygen was generally unavailable for redox chemistry before then as photosynthesis, the process that would evolve to oxidize water to produce dioxygen, was unavailable. Remember that to oxidize water to dioxygen, itself a strong oxidizing agent, requires a stronger oxidizing agent than dioxygen and lots of energy. Fossilized remains of cyanobacteria are found in stromatolites. Using knowledge of how atmospheric oxygen can alter the chemistry of different sulfur isotopes of SO2, it has been shown that O2 did not exist in the atmosphere as a whole above 1 ppm earlier than 2.4 billion years ago, although there might have been isolated pockets with higher concentrations. After that it rose, presumably as a result of cyanobacteria. Before this time, bacteria oxidized a similar molecule, H2S to form elemental sulfur. It could do this through photosynthetic reduction of CO2 by H2S. It is probable that volcanic gases like H2 might have kept oxygen levels from rising between 2.7 billion year ago and 2.4 billion years ago, when its build-up started. Hydrogen in the form of H2 and methane, probably decreased around 2.4 billion years ago as methane with its hydrogen atoms escaped to the upper atmosphere and space. Methane levels would also be decreased by its easy reaction with dioxygen in the presence of UV light to form CO2. This would paradoxically lead to a cooling of the earth and pronounced glaciation as a more potent greenhouse gas, methane, was replaced with a less potent one, carbon dioxide.
Over the next billion years, dioxygen rose to perhaps 0.2 - 2% (compared to the present levels of 20%) Why? Because the early atmosphere was reducing, the added oxygen combined with a large "sink" of reduced metals (like elemental Cu and Fe) or nonmetals (like C and ammonia), preventing a large buildup. Only after these reduced substances were "titrated" did dioxygen build up to present levels. In addition, the oxygen might have increased weathering (by oxidation) of sulfur deposits which can lead to sulfides entering the ocean, where they could precipitate ocean iron ions that are necessary for cyanobacterial chemistry. This would place constraints on cyanobacterial growth until dioxygen levels in the atmosphere increased enough so sulfides were converted to sulfates. This first increase in atmospheric oxygen is often called the Great Oxidation Event as it correlated and presumably caused one of the greatest mass extinctions (of anerobic organisms) of all time.
Around 2.3 billion years ago, as trace dioxygen had accumulated in the atmosphere, redox chemistry changed, although isotope evidence suggest that little dioxgen was found in water. Around 1.8 - 1.5 billion years ago, the earth's atmosphere became somewhat oxygenated, which was also coincident with the development of eukaryotic organisms. Until then, life was restricted to the oceans since there was no ozone to absorb dangerous UV radiation. The buildup of dioxygen in the air must have led to another extinction of anaerobic organisms, since as we shall see, products of oxygen metabolism are very toxic. Some evolved to use dioxygen. Ozone developed, and life could then migrate from the sea to the land. It wasn't until around 600 million years ago that animals arose, however. Was this event associated with the development of a fully oxygenated (20%) atmosphere? Recent evidence, which shows that substantial oxygen wasn't available in the deep sea until about 600 million years, seems to suggest that. Based on analysis of iron compounds in waters in Newfoundland, it appears that oxygen was very low in the sea 580 million years ago, during the Gaskiers glaciation period. Immediately after that it rose to levels consistent with atmospheric dioxygen levels of 15%, levels necessary for large animals. Similar trends in carbon and sulfur isotopes in marine rocks in Oman also suggest large increases in oxygen at the end of the Gaskiers glaciation period. What caused this second great oxygenation event? One possibility is that organic matter was sequestered from reaction with atmospheric dioxygen, as clays bound organic molecules in the ocean and lichens and zooplankton facilitated weather and production of insoluble organic material in the oceans.
Dioxygen is obviously critically important for higher organisms, so an understanding of its chemistry becomes important. This chapter will show that dioxygen is a ground state diradical that has low solubility in aqueous solution, reacts in a kinetically sluggish fashion in oxidation reaction, and forms toxic byproducts as it gets reduced. Life forms hence evolved ways to deal with these problems, including ways to increase its solubility (with dioxygen binding and transport proteins), and enzymes (that could activate it kinetically and also detoxify oxygen by-products). Dioxygen is toxic to many cells. Obligate aerobes die in an oxygen environment as many of their cellular components get oxidized by this excellent oxidizing agent. Several strains of bacteria actually swim away from high levels of dioxygen. A graph showing log of survival vs log pO2 is linear with a negative slope for a variety of organisms, including mice, fish, rats, rabbits, and insects. Pure oxygen can induce chest soreness, coughs, and sore throats in people. Premature infants put in pure dioxygen environments often developed blindness due to retrolental fibroplasia (a build-up of fibrous tissue behind the lens). The trade off for this toxicity is clear. Energy is derived from organic molecule through oxidation. Before dioxygen became available to power aerobic catabolism of reduced molecules like fatty acids and the less reduced sugars, such molecules were only partially oxidized. The glycolytic pathway, found in most organisms, oxidizes glucose (6 Cs) to two molecules of pyruvate (3 Cs). It was only with the availability of dioxygen did pathways evolve (Kreb Cycle, mitochondrial electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation) that allowed pyruvate to be fully oxidized to carbon dioxide, with the release of much more energy.
A2. The Properties of Dioxygen
It is important to understand the properties of dioxygen since oxidation reactions using it power not only our bodies but our entire civilization. We will obviously concentrate on biological reactions, but even these show the same characteristics as non-biological ones.
- oxidation of organic molecules by oxygen is thermodynamically favored but kinetically slow.
- pure oxygen environments are toxic to cells and organisms.
First we will try to understand these properties of oxygen, and then we will see how organisms overcome these problem to use dioxygen.
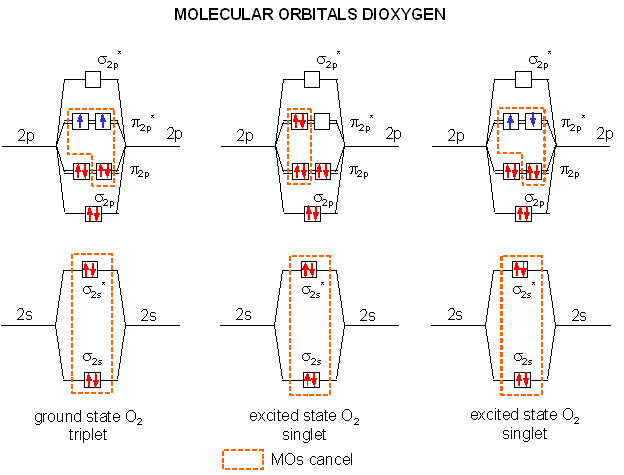
We can understand both of these properties by looking at the molecular orbitals of oxygen and its reduction products as shown in the diagrams below. Ground state oxygen is a diradical, which explains the paramagnetic behavior of oxygen. The two unpaired oxygens each have a spin state of 1/2 for a total resultant spin S of 1, making ground state oxygen a triplet (2S+1) = 3. Organic molecules typically undergo 2 electron oxidation steps. Consider the stepwise oxidation of methane below. The oxidation number of C in methane is -4, -2 in methanol, 0 in formaldehyde, +2 in formic acid, and finally +4 in carbon dioxide, indicating two electron losses in each step.
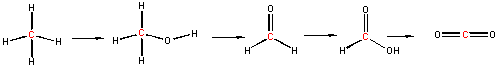
The two electrons lost by the organic substrate are added to oxygen, but since the two lost electrons are spin paired, a spin flip must occur to allow the electrons to enter the unfilled oxygen orbitals. Alternatively, energy can be put into ground state dioxygen to produce excited state singlet oxygen (S=0, 2S+1 = 1). The source of the large activation energy required (about 25 kcal or 105 kJ/mol) to flip the electron spin accounts for the kinetic sluggishness of reactions of dioxygen with organic reactants.
A traditional Lewis structure for ground state dioxygen can not be easily written since the electrons are added in pairs, and dioxygen is a diradical. There are 6 electrons in the sigma molecular orbitals from second shell electrons (two each in σ2s, σ2s*, and σ2p,) and 6 electrons in the pi molecular orbitals from second shell electrons (two each in two different π2p orbitals, and one electron each in two different π2p*), so the net number of electrons in bonding orbitals is 4, giving a bond order (or number of 2). In contrast it is easy to write the Lewis structure of singlet, excited state oxygen, since all electrons can be viewed as paired, with two net bonds (1 sigma, 1 pi) connecting the atoms of oxygen. This Lewis structure will be used to represent singlet, excited oxygen, which should react more quickly with organic molecules. The excited state single on the far right (below) is unstable and decays to the middle singlet state. The middle state is approximately 94.3 kJ/mol higher in energy than the ground state triplet (on the left). In quantum mechanical parlance, the transition from the ground state triplet to the singlet state is forbidden for a number of reasons, making it unlikely that absorption of a photon will induce the transition.
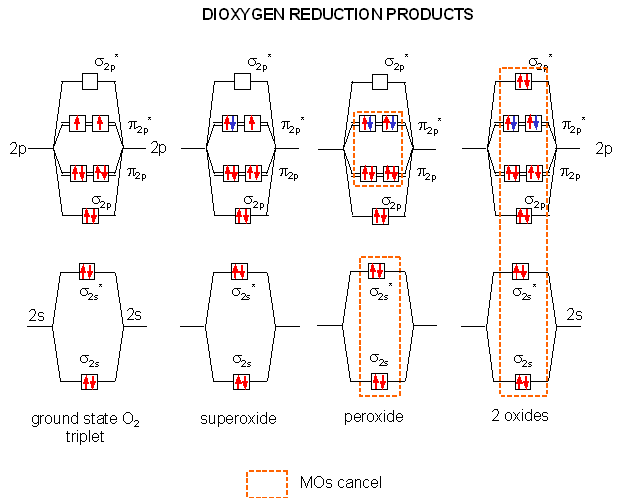
The Reductions of Dioxygen
When oxygen oxidizes organic molecules, it itself is reduced. By adding electrons one at a time to the molecular orbitals of ground state dioxygen we produce the step-wise reduction products of oxygen. On the addition of one electron, superoxide is formed. A second electron produces peroxide. Two more produces 2 separated oxides since no bonds connect the atoms (the number of electrons in antibonding and bonding orbitals are identical). Each of these species can react with protons to produce species such as HO2, H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) and H2O. It is the first two reactive reduction products of dioxygen that make it potentially toxic.
How are the potential problems in oxygen chemistry dealt with biologically?
Kinetic sluggishness: Enzymes that utilize dioxgen must activate it in some way, which decreases the activation energy. Enzymes that use dioxygen typically are metalloenzymes, and often heme-containing proteins. Since metals such as Fe2+ and Cu2+ are themselves free radicals (i.e. they have unpaired electons), they react readily with ground state oxygen which itself is a radical. The molecular orbitals of the metal and oxygen combine to produce new orbitals which for oxygen are more singlet-like in nature. Likewise, dioxygen reacts more readily with organic molecules which can themselves form reasonably stable free radicals, such as flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), as we shall see later.
Dioxygen toxicity: Since toxicity arises from the reduction products of oxygen, enzymes that use oxygen have evolved to bind oxygen and its reduction products tightly (through metal-oxygen bonds) so they are not released into the cells where they can cause damage. In addition, enzymes which detoxify free dioxygen reduction products are widely found in nature. For example:
- superoxide dismutase catalyzes the dismutation (self-redox) of 2 superoxides into dioxygen and hydrogen peroxide;
- catalase converts hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen;
- peroxidase catalyzes the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with an alcohol to form water and an aldehyde
- peroxiredoxins react with peroxides and thioredoxin (a small electron donor) to form water and oxidized thioredoxin .
Finally free radical scavengers such as vitamins A, C, E, and selenium can react with reactive free radicals to produce more stable free radical derivatives of the vitamins and Se. More on this later.
A3. The Reactions of Dioxygen and its Reduction Products
1. Triplet O2 - Ground State:
Figure: Triplet O2 - Ground State
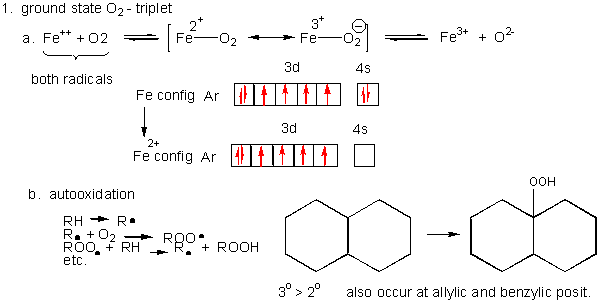
- Metals ions - Metal ions are radicals
themselves, so can react with dioxygen. Ex:
Fe2+ + O2 <--> [ Fe2+-- O2 <--> Fe3+-- O2-.] <--> Fe3+ + O2-. (superoxide) - Autoxidation of organic molecules to
produce peroxides. In this free radical reaction, several reactions
occur, including
RH ---> R. (Initiation)
R. + O2 ---> ROO. (Propagation)
ROO. + RH ---> R. + ROOH (Propagation)
R. + R. ---> R--R (Termination)
ROO. + ROO. ---> ROOR + O2 (Termination)
ROO. + R. ---> ROOR (Termination)
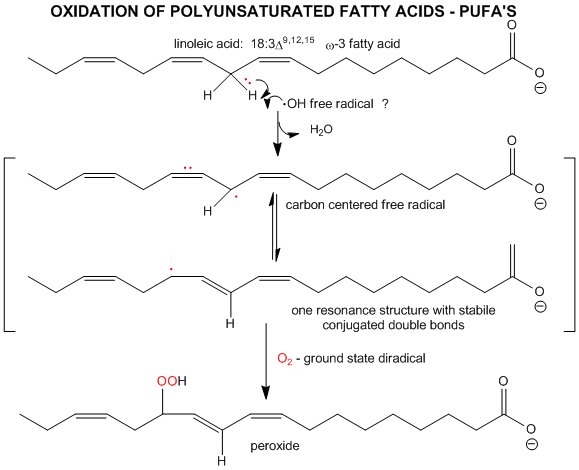
The initiation step above occurs mostly at C atoms which can produce the most stable free radicals (allylic, benzylic position, and 3o > 2o >> 10 carbons). Hence unsaturated fatty acids are extra reactive at the methylene C that separate the double bonds.
Figure: unsaturated fatty acids are extra reactive at the methylene C that separate the double bonds
2. Single O2 - Excited State.
Figure: Single O2 - Excited State
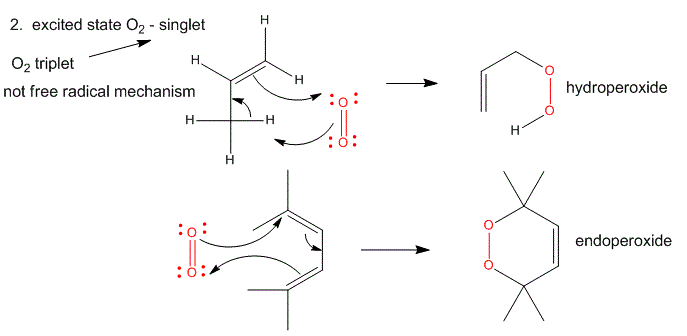
It can be made from triplet oxygen by photoexcitation. Alternatively, it can be made from triplet oxygen through collision with an excited molecule which relaxes to the ground state after a radiationless transfer of energy to triplet oxygen to form reactive singlet oxygen. (This later process accounts for photobleaching of colored clothes when the conjugated dye molecules absorb UV and Vis light, relax by transferring energy to triplet oxygen to form singlet oxygen, which then chemically reacts with the conjugated double bonds in the dye. )
- Alkenes react with oxygen to form hydroperoxides, potentially through a epoxide intermediate
- Dienes reacts with oxygen in a Diels-Alder like reaction to form endoperoxides
3. Superoxide
Figure: Superoxide
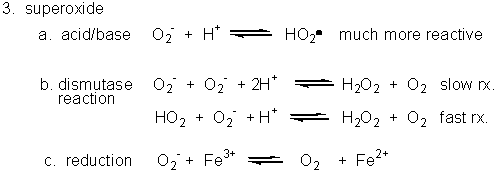
- Dismuation: O2-. + O2-. ---> H2O2 + O2
- Acid/Base: HO2. ----> O2-. + H+ (pKa = 4.8)
- With metal ions: Fe3+ (as in heme) + O2-. ---> O 2 + Fe2+
4. Peroxide
Figure: Peroxide
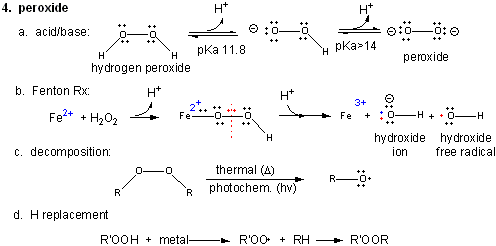
In contrast to dioxygen which contains multiple bonds between the O atoms, peroxide has only one bond. In fact, it is quite weak and requires only 38 kcal/mol to break it. Remember, bonds can be broken in a heterolytic way (both electrons in a bond go to one of the atoms, or in a homolytic fashion, in which the one electron goes to each atom.
- Acid/Base: H2O2 ---> HO2- ---> O22- (pKa1 = 11.8; pKa2 > 14)
- Reaction with Fe2+ - The Fenton Reaction:
(similar to reaction of triplet O2 with Fe2+ above)
Fe2+ + OOH- <--> Fe2+-- OOH <--> Fe2+-- O + OH- <--> Fe3+-- O . <--> Fe3+ + OH. (last step a proton is added). In this reaction, a homolytic cleavage of the O--O bond occurs generating OH- and the hydroxy free radical, OH., which will react with any molecule it encounters. - thermal or photochemical homolytic cleavage of peroxide. This forms alkoxide free radicals which reacts like the hydroxy free radical.
- Reactions with alkyl groups in the
presence of metal ions such as Cu, Co, or Mn:
RH + R'OOH ----> ROOR'
5. Hydroxy free radical:
Figure: Hydroxy free radical
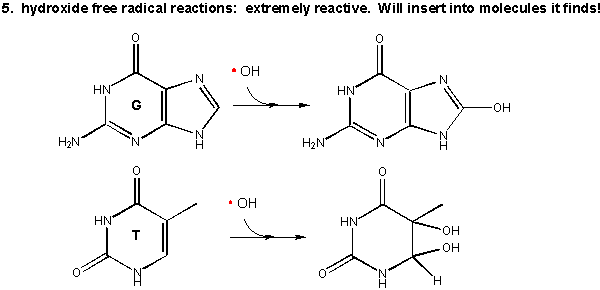
As mentioned above this species is extremely reactive. It will react with any molecule it encounters and does so immediately. It can abstract a H atom leaving another free radical. For example, the hydroxy free radical could extract a hydrogen atom from a polyunsaturated fatty acid to from a carbon-centered radical. A particularly nasty reaction is the insertion of the hydroxy radical into bases in DNA, as shown in the diagram.
A4. Oxidative Modification of Proteins
Oxidative Modification of Proteins:Figure: Oxidative Modification of Proteins
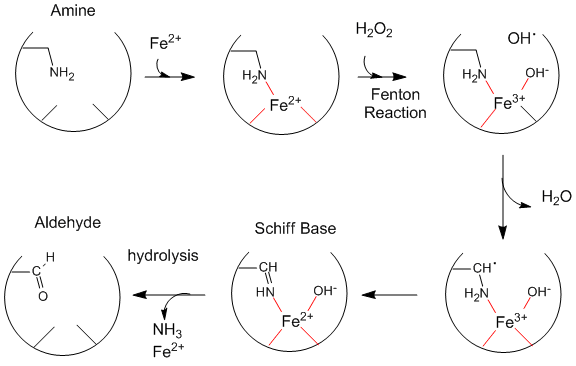
Oxidized levels of proteins (as evidenced by increased levels of aldehydes) increase dramatically with age (especially after age 40 ). The reactions seem to be catalyzed by metals and may proceed by generation of hydroxy free radicals. Diseases associated with premature aging (Werner's Syndrome, another link to Werner's Syndrome, Progeria) show very high levels of oxidized proteins at an early age. Fibroblasts from 10 yr. old children with progeria have levels of oxidized proteins usually not seen until the age of 70. Beta amyloid protein deposits (found in Alzheimer's and Down's Syndrome) cause neurotoxicity and death, partly by increasing superoxide production by endothelial cells, causing vasoconstriction/dilation, and ultimately disease progression. Beta amyloid aggreagates appear to increase H2O2 levels, in a process facilitated by Fe2+ and Cu+. Free radical scavengers (antioxidants) help to prevent this damage. Recent studies suggest that vitamin E may delay the symptoms of Alzheimers.
Lou Gehrigs Disease (Amyotrophic Lateral Schlerosis) is a disease of progressive motor neuron degeneration, which affects 1/100,000 people, and is 10-15% familial. Of the familial cases, about 25% have a mutation in superoxide dismutase I, a copper-zinc enzyme. About 2-3% of ALS patients carry 1 of 60 different dominant mutations in this enzyme. Mutations often decrease the stability of the protein which decreases Zn2+ affinity 5-50 fold. The A4V mutation (valine at amino acid 4 substituted for Ala) has the weakest Zn affinity and causes rapid disease progression. In the absence of Zn2+, the apoprotein somehow seems to induce cell death in neurons. This superoxide dismutase also expresses a second activity. It also acts as a peroxidase which takes ROH + H2O2 to form an RHO (an aldehyde) plus water. In some cases, the enzyme retains normal activity against superoxide but altered peroxidase activity.
Is your hair going white?: Wood et al have shown that millimolar concentrations of hydrogren peroxide build up in hairs that have grayed and whitened. This was associated with a decrease in catalase and in increases in Met oxidation (to Met-sulfoxide) in proteins, also associated with a decrease in the repair enzyme Met-sulfoxide reductase, Met 374 in the active site of tyrosinase, an enzyme required for production of melanin in hair follicles, is also damaged, leading to lack of melanin, a pigment necessary for hair coloration and "senile hair graying".
ROS and Protein Folding
As discussed in Chapter 2D: Protein Folding in Vitro and in Vivo, the cytoplasm has sufficient concentrations of "β-mercaptoethanol"-like molecules (used to reduce disulfide bonds in proteins in vitro) such as glutathione (γ-Glu-Cys-Gly) and reduced thioredoxin (with an active site Cys) to prevent disulfide bond formation in cytoplasmic proteins. Disulfide bonds in proteins are typically found in extracellular proteins, where they serve to keep multisubunit proteins together as they become diluted in the extracellular milieu. These proteins destined for secretion are cotranslationally inserted into the endoplasmic reticulum (see below) which presents an oxidizing environment to the folding protein and where sugars are covalently attached to the folding protein and disulfide bonds are formed (see Chapter 3D: Glycoproteins - Biosynthesis and Function). Protein enzymes involved in disulfide bond formation contain free Cys which form mixed disulfides with their target substrate proteins. The enzymes (thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases, protein disulfide isomerases) have a Cys-XY-Cys motif and can promote disulfide bond formation or their reduction to free sulfhydryls. They are especially redox sensitive since their Cys side chains must cycle between and free disulfide forms.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can significantly affect redox chemistry, and if present in excess can place the cell in a condition of "oxidative" stress. ROS can indiscriminately oxidize lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins, but more specifically, they may also oxidize proteins involved in creating and maintaining the normal disulfide bond formation in proteins. As the concentration of ROS increase, the concentration of cytoplasmic proteins with incorrect disulfides should increase. Using a two dimension PAGE system (first dimension run under nonreducing and the second reducing conditions) of neural cell proteins derived from cells exposed to normal and differing oxidative conditions (hydrogen peroxide or decreased intracellular glutathione levels, Cumming et al showed that oxidizing stress increased the levels of disulfide bonds in redox sensitive enzymes and, unexpectedly, among other cytoplasmic proteins involved in many aspects of life, effecting the activity of many cellular processes, suggesting that disulfide bond formation may have not only a structural but regulatory role.
A5. Oxidative Modification of Lipids:
Figure: Oxidative Modification of Lipids

The initial stages of cardiovascular disease appear to involve the development of fatty acid streaks under the artery walls. Macrophages, an immune cell, have receptors which appear to recognize oxidized lipoproteins in the blood, which they take-up. The cells then become fat-containing foam cells which form the streaks. Oxidation of fatty acids in lipoproteins (possibly by ozone) could produce lipid peroxides and to protein oxidation in lipoproteins. Cortical neurons from fetal Down's Syndrome patients show 3-4 times levels of intracellular reactive O2 species and increased levels of lipid peroxidation compared to control neurons. This damage is prevented by treatment of the neurons in culture with free radical scavengers or catalase.
Figure: oxidized LDL uptake
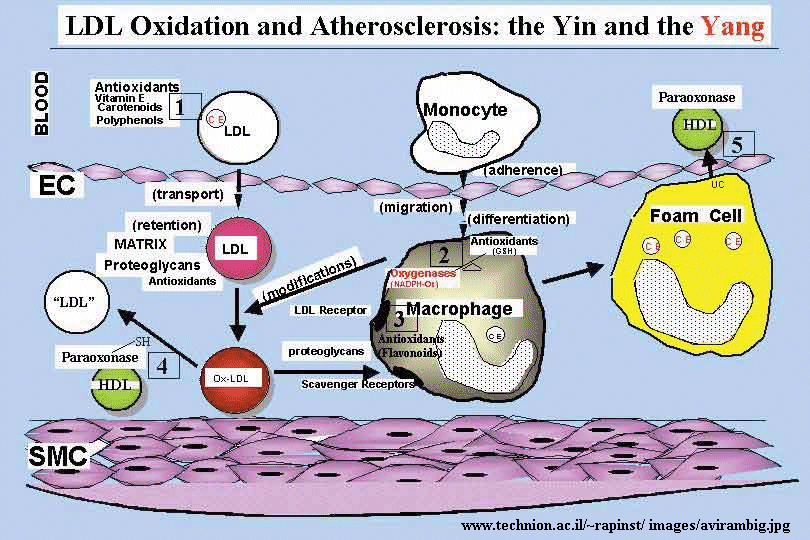
A recent study of peroxiredoxins by Neumann et al showed the importance of these gene products in mice. Peroxidredoxins (which catalyze the conversion of a peroxides and thioredoxin into water and oxidized thioredoxin) are small proteins with an active site cysteine and are found in most organisms. Transcription of the mammalian peroxiredoxin 1 gene is activated by oxidative stress. They inactivated the gene which produced a mouse that could reproduce and appeared vital, but which had a shortened lifespan. These mice developed severe hemolytic anemia and several types of cancers. High levels of reactive oxygen species and resulting increased levels of oxidized proteins were found in red blood cells of the knockout mice with anemia. High levels of 8-oxoguanine, resulting from oxidative damage to DNA, were found in tumor cells.
A6. Oxidative Modification of DNA
Significant evidence suggests oxygen free radicals are linked to aging and diseases. Mutations caused by hydroxylation reactions (presumably from the generation of hydroxyl free radicals as shown above) can potentially lead to cancer. Recently it has been shown that mitochondrial DNA is more susceptible to oxidation that is nuclear DNA. Human mitochondria has its own small genome (16.5 Kb compared to the nuclear genome of 3 Gb) which code 13 protein subunits involved in respiration, 22 tRNAs and two ribosomal RNAs. (The mitochondria presumably are vestiges of a bacteria which invaded an early cell and established a symbiotic relationship with the cell). A recent study has shown that there is an inverse correlation of oxidized mitochondrial DNA [8-oxoG] with maximal life span of an organism, but this correlation is not seen with nuclear DNA. Presumably the nuclear DNA is somewhat protected from oxidative damage since it is bound to histone proteins (which form nucleosome core particles with DNA) and by DNA repair enzymes. DNA repair enzymes that are encoded in the nucleus are found in the mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA is package with mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM). Examination of human bladder, head and neck and lung primary tumors reveals a high frequency of mitochondrial DNA mutations. In addition most dioxygen use by the cell occurs in the mitochondria. Hence this organelle probably faces the highest concentration of toxic oxygen reduction products. Recently, the crystal structure of an enzyme, adenine DNA glycosylase (MutY), that repairs 8-oxyG modified DNA has been determined in complex with the oxidatively damaged DNA. If not repaired, the 8-oxyG base pairs with adenine instead of cytosine, causing a GC to AT mutation on DNA replication.
![]() Jmol: Updated Adenine DNA glycosylase:8-oxyG DNA complex
Jmol14 (Java) |
JSMol (HTML5)
Jmol: Updated Adenine DNA glycosylase:8-oxyG DNA complex
Jmol14 (Java) |
JSMol (HTML5)
Although oxidative damage in mitochondria clearly can promote premature aging, other independent mechanisms may also. In a recent study, Kujoth et al. developed a mouse model that expressed a mutant form of mitochondrial DNA polymerase that was defective in the proofreading activity of the enzyme. These mice displayed premature aging but showed no increased levels of oxidized mitochondrial lipids or hydroxylated G residues in mitochondrial DNA. They did show significant activation of a cytosolic enzyme called caspase-3, which when active lead to the programmed death of cells (a process called apoptosis). This calcium-activated aspartic acid proteases (with an active site Asp) is activated by binding mitochondrial cytochrome C that has "leaked" into the cytoplasm from its normal location in the intermembrane space in mitochondria. The process is usually associated with DNA damage (mutations, fragmentation) that would arise if the proofreading function of DNA polymerase was defective. This was indeed found in these mice.
Oxidative damage to biomolecules might not initiate aging and disease processes, but rather might be a secondary effect of other initiating events. . Reversing or preventing oxidative damage might slow the progression of aging and disease. Aging is a complex feature of organisms and would be expected to have complex causes and biological effects. At the organismal level, aging has been studied in the round worm C. elegans which lives for only a few weeks. Genetic analyses can be easily used to find gene alterations associated with premature aging. One hormonal system that has recently been associated with aging in eukaryotes (and in C. elegans) involves the signaling pathways for insulin and insulin growth factor I (IGF-1), which regulate carbohydrate, lipid, and reproductive pathways in C. elegans. Mutations that decrease signaling from this pathway increase C. elegans life span. These mutations lead to increased activity of the DAF16 transcription factor, which upregulates the expression of many genes. In contrast, wild type organisms, when exposed to insulin or IGF-1, decrease the activity of DAF16. Using DNA microarrays, investigators determined which DAF16-controlled genes were upregulated in mutant worms in the mid-life point of the organism. These genes included, among others, peroxisomal and cytosolic catalase, Mn-superoxide dismutase, cytochrome P450s, metallothionein-related Cd-binding protein, and heat shock proteins. We will investigate the function of several of these gene products in the next section, but needless to say, they are all involved in cellular responses to stress, often involving dioxygen metabolites. Over expression of mitochondrial catalase in mice increased their lifespan by 20%. It has also been showed that decreased levels of insulin-like growth factor also promote longevity in mice, indicating again that mechanisms in addition to oxidative damage by ROS are involved in aging.
A7. Biological Uses for Reactive Oxygen Species - ROS
ROS can be used in the body as defense mechanisms. The can be generated by immune cells that phagocytize (engulf) bacteria and other foreign substances. After uptake, these immune cells undergo an oxidative burst, increasing the amount of dioxygen that they consume, leading to production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide which can be used to kill the engulfed bacteria. Recent articles by Wentworth et al. go even farther. They demonstrated that antibody molecules (protein which bind to foreign molecules and target them for clearance or further immune response) can also generate ROS when they bind to their target. Such an outcome was totally unexpected, but not inconsistent with the observation that antibodies can have catalytic activity if made against transition state analogs of substrates. Over 100 different antibodies were found to generate hydrogen peroxide through the reaction of singlet oxygen (possibly generated by phagocytotic neutrophils during oxidative bursts) with water to form H2O2. (We have previously discussed the idea that singlet O2 can be generated from ground state O2 by excitation through UV light or through collisional activation with an excited state chromophore - a conjugated alkene or aromatic molecule). They postulate the following reaction to form hydrogen peroxide. The oxygen in the peroxide comes from water, as shown by labeling water with 18O:
2H2O + 1O2 (singlet oxygen) --> H2O3 + H2O --> H2O2 + ?
Antibodies show this effect to a much greater extent that other proteins studied. Using UV irradiation as a source of energy, the rate of production of H2O2 was linear with time, but decreased from the initial rate as H2O2 concentrations increased. If it was removed with catalase, the initial rate returned to normal, suggesting that H2O2 was a product inhibitor of the reaction. The reactions also saturated with dioxygen as well. The maximal wavelength of UV irradiation to produce H2O2 was identical to the maximal wavelength of absorbance for tryptophan in the protein. The excited state tryptophan presumably deexcites by energy transfer to triplet dioxygen (3O2 ) in much the manner described earlier for photobleaching. A significant source of electrons needed to be found to account for the production of so much H2O2 which if it was made from singlet oxygen would require 2 electrons for each H2O2. These numbers of electrons could not come from photooxidation of aromatic amino acids in the protein. Hence they theorized that water would add as a nucleophile to the singlet oxygen, providing the source of electrons required to make H2O2. This reactions would go through the H2O3 intermediate.
In another recent study (Nov. 02), the same team discovered that antibodies can not only produce H2O2 but also ozone. O3 is used in killing pathogens but also might lead to inflammation. In their previous work described above, they generated singlet oxygen in a "non-physiological" way - through UV irradiation of the antibodies. They also didn't show that the ROS produced can kill bacteria without any other immune mediators. They used a new singlet oxygen generating system which led to insufficient peroxide formation to account for the extensive killing of E. Coli that they observed (95%). This led them to look for the generation of a more potent oxidizing agent - which they believe is consistent with the formation of ozone. They also showed that neutrophils were the source of the required singlet oxygen as described above.
In an additional study (Dec 02), the showed that antibodies in the presence of singlet oxygen and in the absence of immune cells or other immune proteins (like complement proteins) can "destroy antigenic target". They also confirmed that ozone is produced by antibodies during bacterial killing by neutrophils (which produce singlet oxygen) and in inflammatory states. Signaling through ozone might amplify other immune molecules that signal the activation (or hyperactivation) of the immune system.
In a subsequent study (Nov. 03) they examined the involvement of ozone (generated from antibodies in the presence of singlet O2 from neutrophils) in the oxidation of lipoproteins, a process which has been associated with atherosclerosis in coronary arteries. First they tested if ozone could be generated by atherosclerotic lesions treated with phorbol myristate acetate. 14/15 plaques produced ozone, as evidenced by the photobleaching of the dye indigo carmen to isatin sulfonic acid. This conversion, known to be specific for ozone, is shown below.
Figure: Conversion of indigo carmen to isatin sulfonic acid
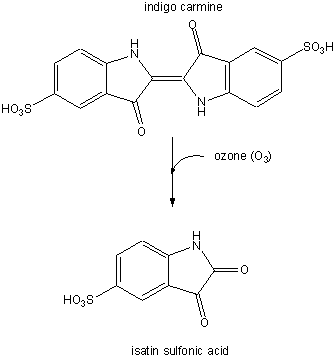
They then looked for the telltale signature of the reaction of ozone with plaque cholesterol (cleavage of the Δ5,6 double bond to form 5,6-secosterol as shown below and found it. This reaction is known not to occur with other oxygen oxidants, including both triplet and singlet oxygen, superoxide, and the hydroxyl free radical. A secondary reaction product aldol condensation product was also produced. They named these new products atheronals.
Figure: Cholesterol/ozone reaction
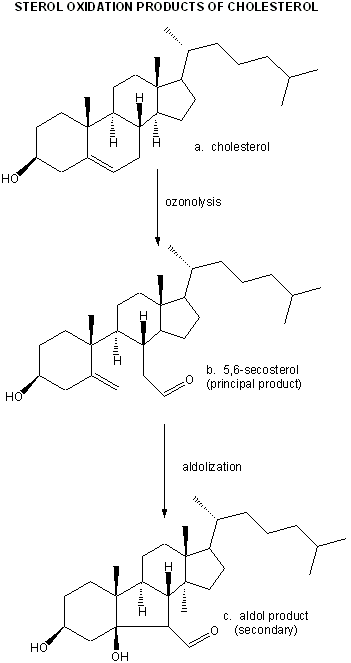
Figure: Ozonolysis mechanism
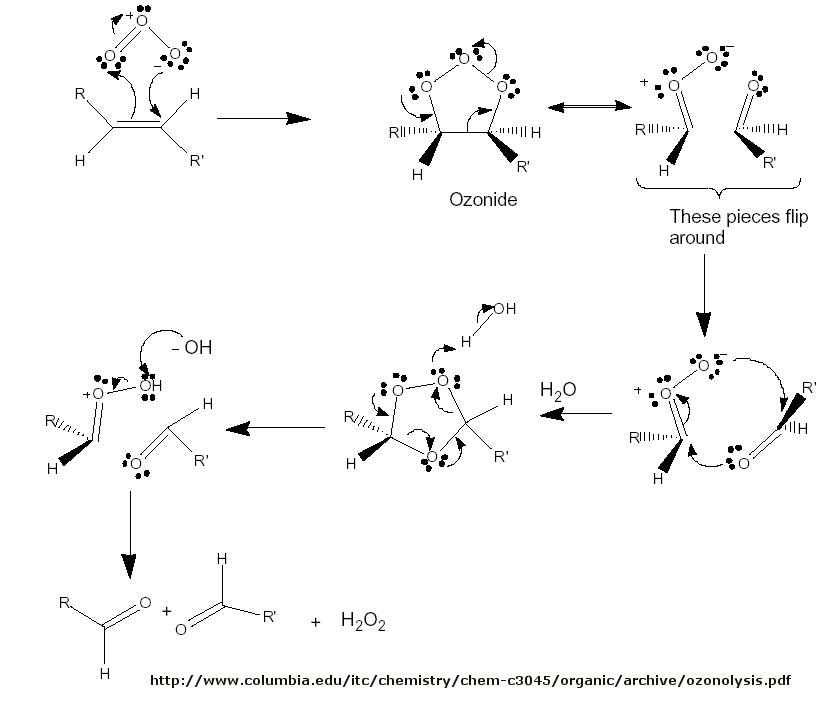 Figure:
Figure:
Significant increases in secosterol was found in plaques treated with the phorbal ester. 6 of 8 patients with atherosclerosis had elevated plasma levels of the secosterol, while only 1 of 15 of control patients did. They also showed that these ozone products caused normal macrophages to fill with cholesterol (presumably from oxidized LDL), and that the structure of the LDL apoprotein B100 changed. These findings might provide a link between the immune system and cholesterol in the generation of cardiovascular disease.
A8. Just Say NO - The Chemistry of Nitric Oxide
In the last decade, the role of another gaseous free radical, nitric oxide (.NO) has become apparent. This molecule is synthesized biologically through the action of an inducible heme enzyme, nitric oxide synthase, which forms NO by the oxidation by dioxygen of the guanidino group of Arg, which gets converted to citrulline. .NO is soluble and can diffuse through cell membranes into the cytoplasm, where it has a myriad of effects in signal transduction pathways. However, it can also be metabolized to form reactive nitrogen intermediates (much as with dioxygen) which can be deleterious to the body, if they damage native biomolecules, or advantageous, when they are used by immune cells like macrophages in the destruction of engulfed bacteria.
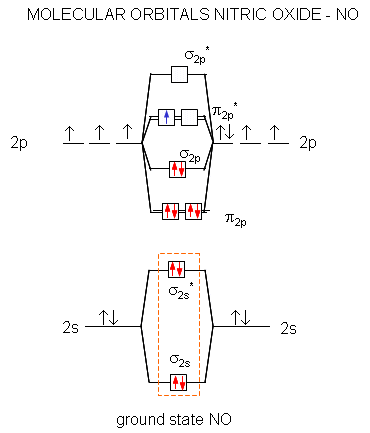
A molecular orbital diagram of .NO shows it to have a bond order of 2.5 and one unpaired electron in a π2p* antibonding orbital (hence the notation .NO).
Figure: Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO
Here are some of the relevant reactions of NO and its reactive nitrogen intermediates (RNI):
-
The high energy electron π2p*can leave on oxidation of NO to form the nitrosyl ion, NO+. The bond order in NO+ is three suggesting strong interactions between the N and O atoms.
-
.NO (oxidation number of N of +2) is thermodynamically unstable and can disproportionate or dismutate (like superoxide) in a self redox reaction to form nitrous oxide (N2O) and nitrogen dioxide (.NO2), with oxidation number for N of +1 and +4, respectively.
-
In acidic condition .NO can be oxidized to nitrite (NO2-) which can be protonated to form nitrous acid (HNO2).
-
Nitrous acid can disproportionate or dismutate to form .NO and the radical .NO2 which can be protonated to ONOOH with a pKa of 6.5.
-
.NO can react with superoxide (.O2-) faster than any other molecule to form peroxynitrite, ONOO- . .NO and superoxide (.O2-) are both produced by cells during infllammation, leading to increased levels of peroxynitrite.
-
The O-OH bond in protonated peroxynitrite (ONO-OH) can be cleaved either heterolytically to produce NO3- and H+ (70%) or homolytically to produce the radical .NO2 and the highly reactive .OH free radical (30%).
- The deprotonated form of peroxynitrite (ONOO-) can oxidize organic molecules, especially thiols and CO2. When it reacts with CO2, it can form either NO3- and CO2 (65%) or CO3.- and .NO2 (35%). These latter products can oxidize organic molecules in one electron steps. Peroxynitrite can also oxidize protein, DNA, and lipids.
- .NO2 and peroxynitrite can interact with Tyr side chains in proteins to form nitrated proteins (Tyr-NO2), whose presence reflects inflammation.
Macrophages make use of RNIs in the killing of engulfed bacteria. How does one of humankinds greatest foes, Mycobacteria tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis, avoid this killing mechanism? It is estimated that the bacteria resides persistently in latent form in 2 billion people. If it becomes activated, it becomes one of the greatest killers. Consider the following table:
Killer Diseases through time (Scientist, June 2, 2003)
| Historic Pandemics | cases | deaths |
| Justinian Plaque (6th centr.) | 142 million (on 70% mort) | about 100 mill |
| China Plaque (Bubonic) 3rd Pandemic (1896-1930) | 30 milion | 12 milion |
| Spanish flu 1918-19 | 1 billion | 21 million |
Pandemics Today
| Pandemics Today | cases/yr | deaths/yr |
| Malaria | 300-500 mil | 1 million |
| TB | 8 mill | 2 mill |
| AIDS | 6 million | 3 mill |
People infected with the bacteria but without clinical symptoms must mount a sufficient enough immune response to restrain proliferation of the bacteria, but not enough to clear it from the body. Immune-compromised people (transplant recipients taking anti-rejection drugs or AIDS patients) have more difficulty in holding the bacteria at bay. One immune response mediator which restrains bacterial growth is the soluble protein interferon γ (a protein cytokine released by immune cells). This protein induces synthesis of nitric oxide synthase, producing .NO, which through the reactions listed above, can damage bacterial macromolecules.
Bacteria are "digested" in acidic phagosomes of the macrophage. Nitrite formed in the acid conditions from .NO (generated by inducible NO synthase) forms .NO2 and peroxynitrite which have antibacterial properties (better than anti-Tb drugs). Mutant mice that can not synthesize inducible NO synthase have little defense against the bacteria. Darwin e al. exposed the bacteria to sources of nitrite at pH conditions typical of macrophage phagosomes and found mutants sensitive to the RNIs. The mutations involved protein of the bacterial proteasome, a complex multi-protein complex which proteolyzes unwanted (presumably damaged) cellular proteins.
Bacterial genes encoding proteins associated with the bacterial proteasome seem to confer resistance to the effects of macrophage-inducted RNI production. The macrophage proteasome, like other eukaryotic proteasomes, is a cytoplasmic protein complex which degrades damaged cytoplasmic proteins. Although the mechanism is uncertain, the bacterial proteasome may rid the bacteria of nitrated or otherwise oxidized (damaged) proteins or remove the nitrate and facilitate refolding of the damaged protein.
![]() Peroxynitrite
in health and disease
Peroxynitrite
in health and disease
![]() Nitric
Oxide Synthases: Structure, Function, and Inhibition
Nitric
Oxide Synthases: Structure, Function, and Inhibition
A9. Antioxidant and Disease
If oxidative damage by dioxygen reduction products can cause disease, maybe antioxidant vitamins (E, C, A), which can form reasonably stable free radical, can protect the body from their effects.
Figure: antioxidant vitamins (E, C, A)
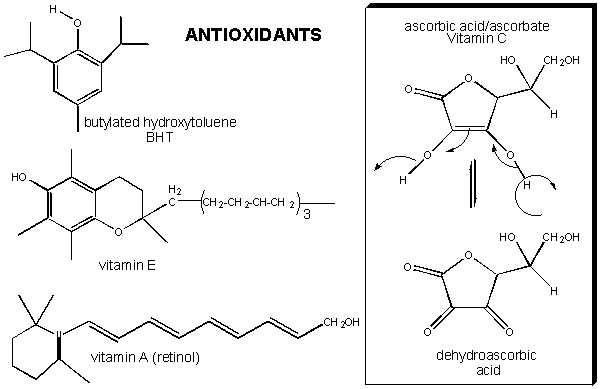
It has been shown that these vitamins can help protect white blood cells from DNA damage arising from hydroxy free radicals. Vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin carried in circulating lipoproteins, can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, presumably by preventing oxidation of lipids and proteins in lipoproteins. Vitamin E and C, along with a common food additive, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) can form stable free radicals (formed possibly by abstraction of a hydrogen atom by hydroxyl free radicals) since the lone electron is stabilized by resonance and the the O-centered resonant form is sterically restricted from intermolecular interactions which could propagate the free radical chain reactions.
TBA: Recent literature showing link to antioxidants and cancer
![]() Human
mitochondrial protein database from the NIST
Human
mitochondrial protein database from the NIST
A10. Hypoxia
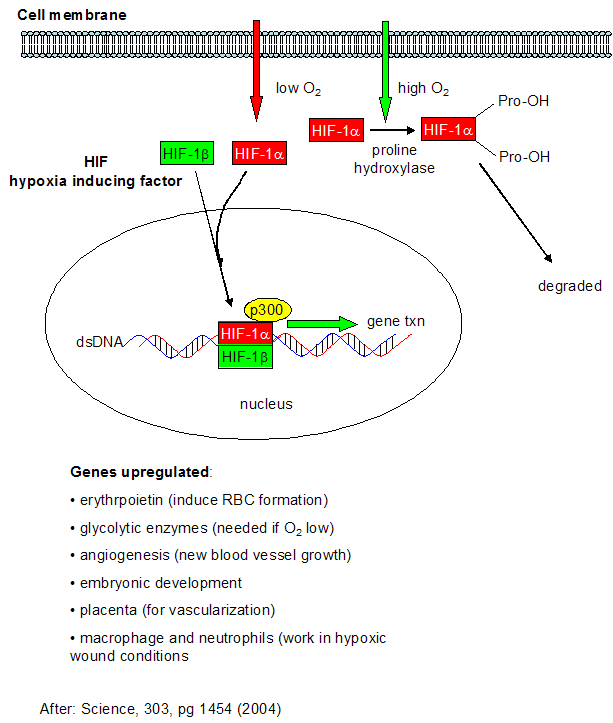
We have spend much time studying how the body deals with and utilizes the toxic byproducts of dioxygen reduction. What happens when the body doesn't get enough dioxygen - a condition call anoxia (no dioxygen) or hypoxia (too little dioxygen)? This might occur in muscles undergoing vigorous exercise, and in the brain and heart when clots occlude blood flow to these organs (as occurs in most strokes and heart attacks). Under low dioxygen concentrations, a family of protein transcription factors called hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) become activated. The functional proteins appears to be a dimer of HIF-α and HIF-β. In contrast to the concentration of the beta form, the activity of HIF-α is increased under low dioxygen concentrations. HIF-α concentration is regulated not at the transcriptional level, but through proteolysis of the protein. In the presence of abundant dioxygen, HIF-α is hydroxylated at two Pro residues by the enzyme prolyl hydroxlase. This post-translational modification targets the protein for proteolysis (through ubiquitination by the VHL protein and subsequent cleavage by the proteasome). A second independent pathway in rapidly growing tissue leads to increased expression of HIF-α even in the presence of dioxygen. This could be beneficial to cells since rapidly growing tissue, especially tumor cells, might be expected to experience low oxygen conditions.
Figure: Cell response to hypoxia
A11. Links and References
- Wood, J. et al. Senile hair graying: H2O2-mediated oxidative stress affects human hair color by blunting methionine sulfoxide repair. FASEB Journal. Published online before print February 23, 2009 as doi: 10.1096/fj.08-125435
- Kerr, R. A Shot of Oxygen to Unleash the Evolution of Animals. Science 314, 1529 (2006)
- Falkowski, P. Tracings Oxygen's Footprint on Life's Metabolic Evolution. Science 311, 1724 (2006)
- Kerr, R. The Story of O2, Science. 308, 1730 (2005)
- Schriner, S. et al. Extension of Murine Life Span by Overexpression of Catalase Targeted to Mitochondria. Science 308, pg 1909 (2005)
- Kujoth, G.C. et al. Mitochondrial DNA Mutations, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Mammalian Aging. Science. 309, pg 481 (2005)
- Mattson, M. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 430, pg 631 (2004)
- Marx, J. How cells endure low oxygen. Science. 303, pg 1454 (2004)
- Fromme, J.C. et al. Structural basis for removal of adenine mispaired with 8-oxoguanine by MutY adenine DNA glycosylase. Nature. 427, pg 652 (2004).
- Cumming, R. et al. Protein Disulfide Bond Formation in the Cytoplasm during Oxidative Stress. J. Biol. Chem., 279, 21749 (2004)
- Darwin, K. Nathan, C. et al. The proteasome of mhycobacterium tuberculosis is required for resistance to nitric oxide. Science. 302, pg 1963 (2003)
- Wentworth, P. et al. Evidence for Ozone Formation in human atherosclerotic arteries. Science. 302, pg 1053 (2003)
- Neumann et al. Essential role for the peroxiredoxin Prdx1 in erythrocyte antioxidant defence and tumor suppression. Nature. 424, pg 561 (2003)
- Murphy, C. et al. Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 424, pg 277 (2003)
- Wentworth, P. et al. Evidence for Antibody-Catalyzed Ozone formation in bacterial killing and inflammation. Science. 298, pg 2195, 2143 (2002)
- Wentworth et al. Antibodies Kill by Producing Ozone. Science. 298, pg 1319 (2002); www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/1077642.
- Lin et al. Calorie restriction extends Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan by increasing respiration. Nature. 418, pgs. 287 , 344 (2002) (counterintuitive finding that increased O2 consumption which leads to increased free radical production doesn't decrease lifespan)
- Wentworth et. al. Antibody Catalysis of Oxidation of Water. Science: 293, pg 1806 (2001)
- Catling et al. The Rise of Atmospheric Oxygen. 293, pg 819, 839 (2001)
- Lee et al. Vitamin C-Induced Decomposition of Lipid Hydroperoxides to Endogeneous Genotoxins. Science. 292, pg 2083 (2001)
- Prinn etl al. Evidence for Substantial Variations of Atmospheric Hydroxyl Radicals in the Past Two Decades. Science. 292. pg 1882 (2001)
- Finkel & Holbrook. Oxidants, Oxidative Stress and the Biology of Aging. Nature. 408. pg 239 (2000)
- Oxygenating the atmosphere. Nature. 410. pg 317 (2001)
- The Story of O Nature. 410. pg 862 (2001)
- Kirkwood and Austad. Why Do We Age? Nature. 408, pg 233 (2000)
- Xiong et al. When did photosynthesis emerge on Earth? Science. 289. pg 1702or3, 1724 (2000)
- Salvemini et al. A Nonpeptidyl mimic of superoxide dismutatse with therapeutic activity in rats. Science. 286. pg 304 (1999)
- Head et al. Bioluminescence illuminated (strucure of aequorin - calcium activated photoprotein) Nature 405, pg 291, 372 (2000)
- Chipping Away at the Causes of Aging (use microarrays to study gene expression in fibroblasts from normal people and patients with progeria). Science. 287, pg 2390, 2486 (2000)
- Lee et al. Gene Expression profile of aging and its retardation by caloric restriction. Science. 295, pg 1390 (1999)
- Early Life thrived despite earthly travails. Science. 284, pg 2111 (1999)
- Marshall et al. Nitrosation and oxidation in the regulation of gene expression. (post-translational oxidation of transcription factors- possibly at thol residues - might regulate gene expression. FASEB Journal. 14, pg 1889 (2000)

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.