Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 1 - LIPID STRUCTURE
C: Dynamics of Membrane Lipids
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
02/12/2016
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 1C: After class and this reading, students will be able to
|
C2. Lipid Distribution in Cells
To understand movement of lipids in an actual cell, a better understanding of lipid synthesis and trafficking in cells is important. The table below shows the distribution of four classes of lipids in a macrophage, a type of immune cells (Andreyev, A.Y. et al) while the following figure shows how the lipids composition of membranes organelle membranes.
Table: Distribution of Lipids in Resting Macrophage
|
Lipid Categories |
Nucleus |
Mitochon-dria |
Endo. Reti. |
Plasma Memb |
microsome |
cytosol |
Whole cell |
|
Glycero-phospholipids |
149 |
152 |
150 |
151 |
142 |
109 |
155 |
|
Prenol lipids |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
Sphingolipids |
48 |
47 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
47 |
48 |
|
Sterol lipids |
13 |
12 |
12 |
13 |
11 |
5 |
12 |
|
Total |
215 |
216 |
215 |
217 |
206 |
166 |
220 |
Figure: Approximate Distribution Phospholipids in Resting
Mammalian Cells
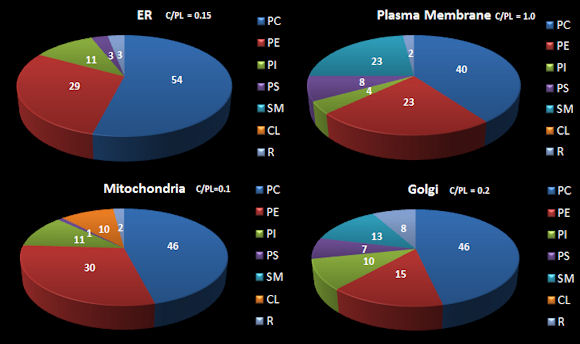
Lipids in membranes are often distributed asymmetrically. The inner and outer leaflet of a biological membrane usually have different PL compositions. For example, in red blood cell membranes, the outer leaflet is composed mostly of sphingomylein (SM) and PC, while the inner leaflet is composed mostly of PE and phosphatidyl serine (PS). This phospholipid contains the amino acid serine linked through its side chain (-CH2OH) to phosphate in position 3 of diacylglyerol. With a negative charge on the phosphate and carboxylate and a positive charge on the amine of PS, this phospholipid is acidic with a net negative charge. All the PS is located in the inner leaftet! This observation will become important latter on, when we discuss programmed cell death. A dying cell will expose PS in the outer leaflet. This is in fact one of the markers of a dying cell.
The membrane lipid composition in an average mammalian cell
| Lipid | % |
| PC | 45-55 |
| PE | 15-25 |
| PI | 10-15 |
| PS | 5-10 |
| PA | 1-2 |
| SM | 5-10 |
| cardiolipin (bis-PG) | 2-5 |
| cholesterol | 10-20 |
Navigation
Return to Chapter 1C: Dynamics of Membrane Lipids
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 1C: Dynamics of Membrane Lipids