Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 8: OXIDATIVE-PHOSPHORYLATION
A: THE CHEMISTRY OF DIOXYGEN
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
04/14/16
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 8A: After class and this reading, students will be able to
|
A9. Antioxidant and Disease
If oxidative damage by dioxygen reduction products can cause disease, maybe antioxidant vitamins (E, C, A), which can form reasonably stable free radical, can protect the body from their effects.
Figure: antioxidant vitamins (E, C, A)
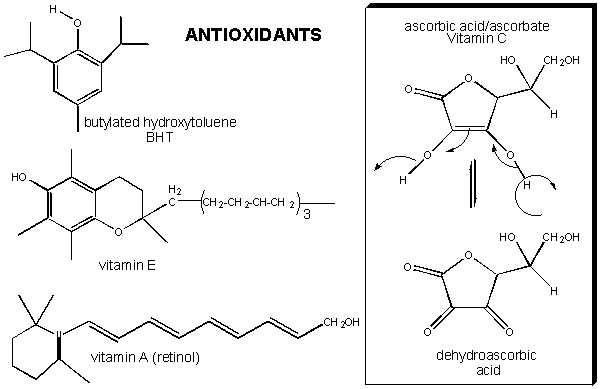
It has been shown that these vitamins can help protect white blood cells from DNA damage arising from hydroxy free radicals. Vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin carried in circulating lipoproteins, can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, presumably by preventing oxidation of lipids and proteins in lipoproteins. Vitamin E and C, along with a common food additive, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) can form stable free radicals (formed possibly by abstraction of a hydrogen atom by hydroxyl free radicals) since the lone electron is stabilized by resonance and the the O-centered resonant form is sterically restricted from intermolecular interactions which could propagate the free radical chain reactions.
TBA: Recent literature showing link to antioxidants and cancer
![]() Human
mitochondrial protein database from the NIST
Human
mitochondrial protein database from the NIST
Navigation
Return to Chapter 8A: The Chemistry of Dioxygen Sections
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 8A: The Chemistry of Dioxygen

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.