Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 9 - SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
C: SIGNALING PROTEINS
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
04/16/16
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 9C:
|
Estonian Translation √ by Anna Galovich
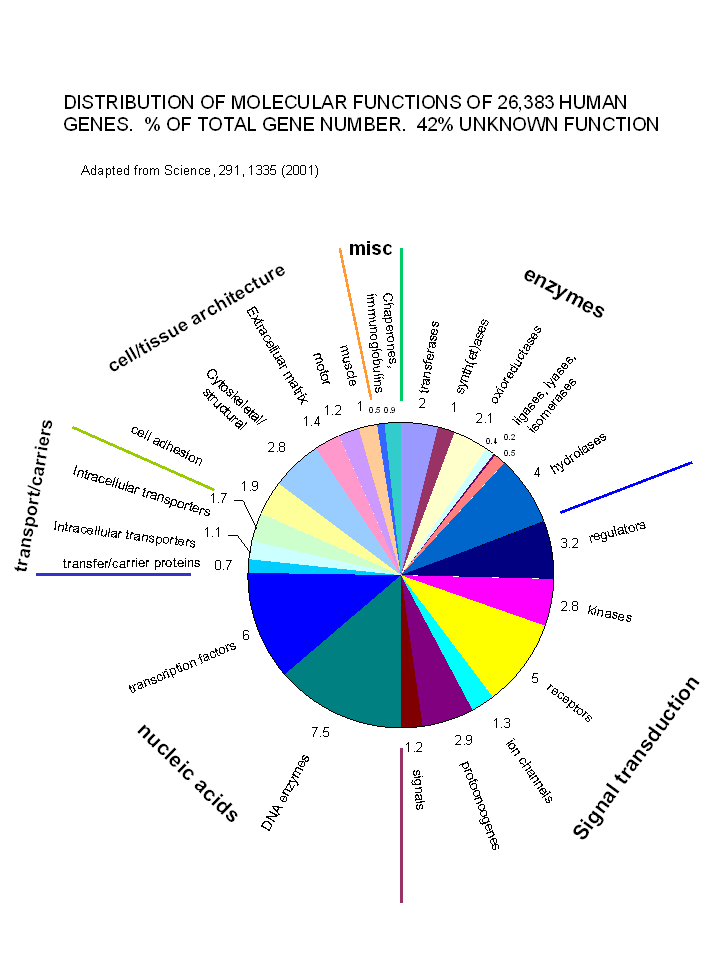
C14. The Human Genome and Signal Transduction
With the determination and annotation of the human genome, it has become very clear that a significant fraction of the human genome (about 40% of the 58% of known genes determined by Venter et. al. and published in Science, 291, 1335, 2001) is devoted directly or indirectly to signal transduction processes. These include signal molecules, receptors, kinases, regulators, protooncogenes and ion channels. The chart below shows the relative distribution of over 26,000 genes of known function (with 42% still of unknown function.
Figure: Distribution of Molecular Functions of 26,383 Genes
Navigation
Return to Chapter 9C. Signaling Proteins Sections
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 9C: Signaling Proteins

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.