Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 9 - SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
C: SIGNALING PROTEINS
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
04/16/16
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 9C:
|
Estonian Translation √ by Anna Galovich
C3. Protein Kinase C (PKC) and calmodulin-dependent kinase (CAM-PK)
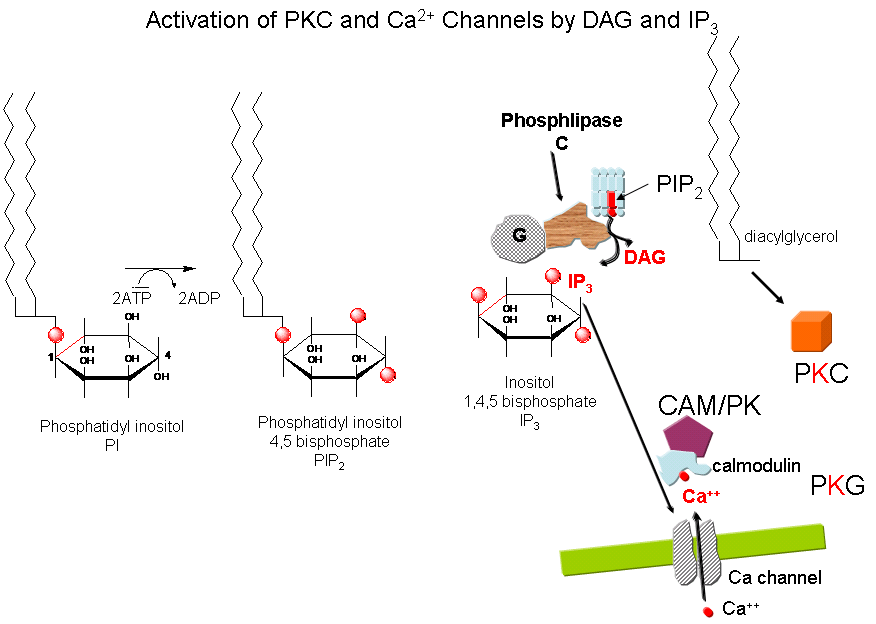
Cascade of Events: A transmembrane receptor WITHOUT ENZYME ACTIVITY binds an extracellular chemical signal, causing a conformational change in the receptor which propagates through the membrane. The intracellular domain of the receptor then binds to an intracellular heterotrimer G protein (since it binds GDP/GTP) in the cell. The G protein dissociates and one subunit interacts with and activates an enzyme - phospholipase C - which cleaves the phospho-head group from a membrane phospholipid - phosphatidyl inositol - 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into two second messengers - diacylglyerol and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). Diacylglycerol binds to and activates protein kinase C (PKC). The IP3 binds to ligand-gated receptor/Ca++ channels on internal membranes, leading to an influx of calcium ions into the cytoplasm. Calcium ions bind to a calcium modulatory protein, calmodulin, which binds to and activates the calmodulin-dependent kinase (CAM-PK). The released calcium ions also activate PKC. As in the previous example, these receptors which interact with G proteins are single polypeptide chains which contain 7 membrane spanning alpha helices. The cycle of degradation and resynthesis of PIP2 is called the PI cycle.
Figure: PI cycle
Some signals that activate phospholipase C and make IP3 and diacylglycerol include: acetylcholine (a different class than the type located at the neuromuscular junction that we discussed in the last chapter section), angiotensin II, glutamate, histamine, oxytocin, platelet-derived growth factor, vasopressin, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Some proteins phosphorylated by PKC include:
Add table.
Some kinases regulated by calcium and calmodulin include: myosin light chain kinase, PI-3 kinase, CAM-dependent kinases. Ca/CAM also regulates other proteins which include: adenylate cyclase (brain), Ca-dependent Na channel, cAMP phosphodiesterase, calcineurin (phosphoprotein phosphatase 2B), cAMP gated olfactory channels, NO synthase, and plasma membrane Ca/ATPase.
Navigation
Return to Chapter 9C. Signaling Proteins Sections
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 9C: Signaling Proteins

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.