NMR3. Symmetry in Spectroscopy
Butane shows two different peaks in the 13C NMR spectrum, below. Note that:
- the chemical shifts of these peaks are not very different from methane. The carbons in butane are in a similar environment to the one in methane.
- there are two distinct carbons in butane: the methyl, or CH3, carbon, and the methylene, or CH2, carbon.
- the methyl carbon absorbs slightly upfield, or at lower shift, around 10 ppm.
- the methylene carbon absorbs at slightly downfield, or at higher shift, around 20 ppm.
- other factors being equal, methylene carbons show up at slightly higher shift than methyl carbons.
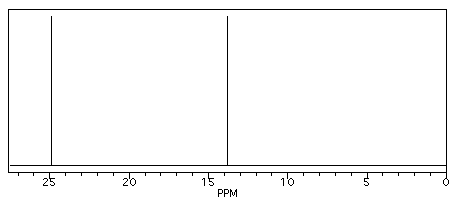
Figure NMR3.1. Simulated 13C NMR spectrum of butane (showing only the upfield portion of the spectrum).
In the 13C NMR spectrum of pentane (below), you can see three different peaks, even though pentane just contains methyl carbons and methylene carbons like butane. As far as the NMR spectrometer is concerned, pentane contains three different kinds of carbon, in three different environments. That result comes from symmetry.
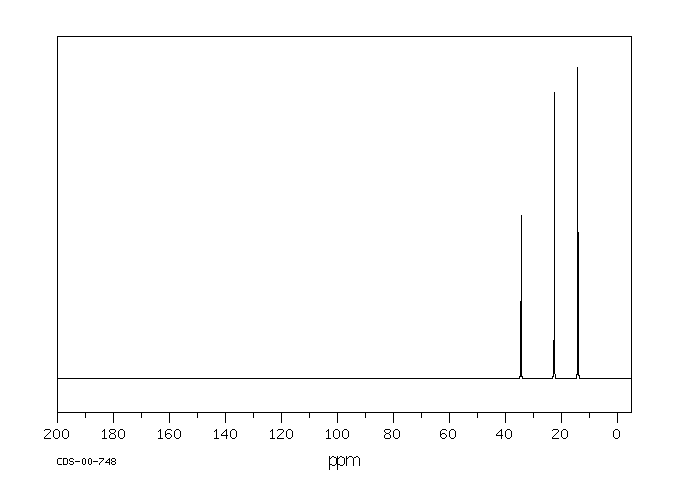
Figure NMR3.2.13C NMR spectrum of pentane.1
Symmetry is an important factor in spectroscopy. Nature says:
- atoms that are symmetry-inequivalent can absorb at different shifts.
- atoms that are symmetry-equivalent must absorb at the same shift.
To learn about symmetry, take a model of pentane and do the following:
- make sure the model is twisted into the most symmetric shape possible: a nice "W".
- choose one of the methyl carbons to focus on.
- rotate the model 180 degrees so that you are looking at the same "W" but from the other side.
- note that the methyl you were focusing on has simply switched places with the other methyl group. These two carbons are symmetry-equivalent via two-fold rotation.
An animation of the structure is provided in the link below. Grab the model with the mouse and rotate it so that you are convinced that the second and fourth carbons are symmetry-equivalent to each other, but the middle carbon is not.
Go to Animation NMR3.1. A three-dimensional model of pentane.
By the same process, you can see that the second and fourth carbons along the chain are also symmetry-equivalent. However, the middle carbon is not; it never switches places with the other carbons if you rotate the model. There are three different sets of inequivalent carbons; these three groups are not the same as each other according to symmetry.
Problem NMR3.1.
Determine how many inequivalent carbons there are in each of the following compounds. How many peaks do you expect in each 13C NMR spectrum?
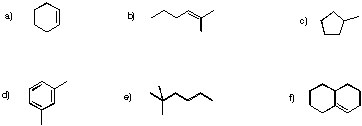
Problem NMR3.2.
Based on an IR spectrum, you have determined that your sample is a saturated hydrocarbon; it contains only C-C and C-H bonds. Assuming a straight chain structure with no branches, what could be the structure in the following cases:
a) 3 peaks in the 13C spectrum
b) 4 peaks in the 13C spectrum
c) 5 peaks in the 13C spectrum
Practically speaking, there is only so much room in the spectrum from one end to the other. At some point, peaks can get so crowded together that you can't distinguish one from another. You might expect to see ten different peaks in eicosane, a twenty-carbon alkane chain, but when you look at the spectrum you can only see seven different peaks. That may be frustrating, because the experiment does not seem to agree with your expectation. However, you will be using a number of methods together to minimize the problem of misleading data.
