Biochemistry Online: An Approach Based on Chemical Logic
CHAPTER 9 - SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
B: NEURAL SIGNALING
BIOCHEMISTRY - DR. JAKUBOWSKI
06/10/14
|
Learning Goals/Objectives for Chapter 9B:
|
B10. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters:
The main inhibitory neurotransmitters are GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, which is made from Glu through decarboxylation of the α-C group) and glycine. The bind to transmiitter-gated chloride channels, which when open hyperpolarize the membrane. Benzodiazepines (like Valium and Librium - anti-anxiety and muscle-relaxing agents) and barbituates (like phenobarbital-hypnotics) bind at allosteric sites and potentiate the binding of each other and GABA.
![]() Updated
Chloride Channel
Jmol14 (Java) |
JSMol (HTML5)
Updated
Chloride Channel
Jmol14 (Java) |
JSMol (HTML5)
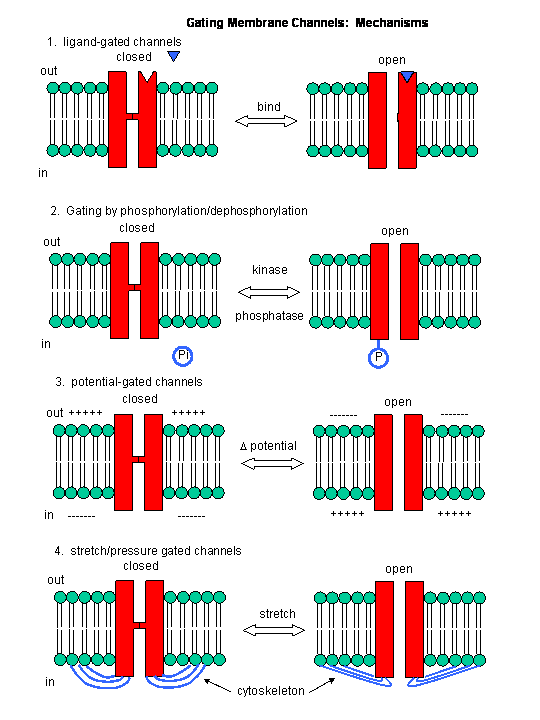
Figure: Mechanisms of Channel Gating
Navigation
Return to Chapter 9B: Neural Signaling Sections
Return to Biochemistry Online Table of Contents
Archived version of full Chapter 9B: Neural Signaling

Biochemistry Online by Henry Jakubowski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.