Cut Site Selection by the Two Nuclease Domains of the Cas9 RNA-guided Endonuclease. Hongfan Chen, Jihoon Choi and Scott Bailey.The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289, 13284-13294 (2014)
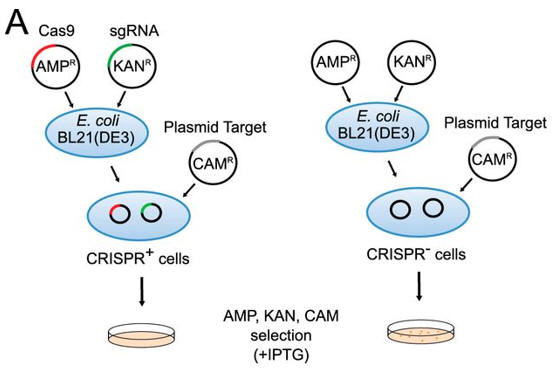
2. To confirm that the identified PAM was functional, investigators needed a selection system. They used a transformation assay in which E. coli cells containing an exogenous type II CRISPR-Cas system were resistant to plasmid transformation, whereas cells lacking the system are competent for transformation. Explain how this system could be used to determine if specific PAM are functional?
a. Figure A shows a schematic representation of transformation assay.

The target plasmid contained protospacer-1 (whose sequence was identical to the first spacer of CRISPR-1), a 2-bp linker, and the identified PAM. The first control plasmid contained only protospacer-1, whereas the second control plasmid lacked both protospacer-1 and PAM. The target and control plasmids were then used to transformed cells. in the presence of IPTG and the appropriate antibiotics.
Why did the investigators add IPTG? What difference would you expect to find in the cells in the left panel compared to the right in their assay?
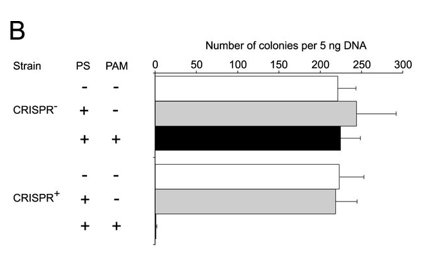
b. Figure 2B shows plasmid transformation by LMG18311 Cas9 and sgRNA in E. coli cells. Transformation efficiency is expressed as cfu per 5 ng of plasmid DNA. Average values from at least three biological replicates are shown, with error bars representing 1 S.D. Interpret and explain results.
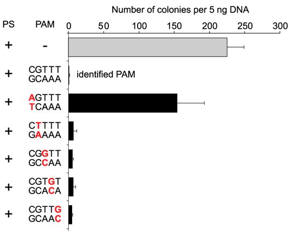
c. For Figure C, the investigators made single nucleotide changes in the PAM sequence of the CRISPR+ plasmid and studied the effect on plasmid transformation efficiency. Interpret he results.
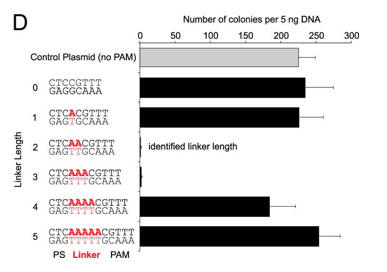
d. For Figure D, the effect of the length of the linker length on plasmid transformation efficiency was studied. PS denotes the protospacer sequence. Interpret the results.